Acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging in diagnostic ultrasound
- PMID: 23549529
- PMCID: PMC3679553
- DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2617
Acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging in diagnostic ultrasound
Abstract
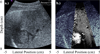
The development of ultrasound-based elasticity imaging methods has been the focus of intense research activity since the mid-1990s. In characterizing the mechanical properties of soft tissues, these techniques image an entirely new subset of tissue properties that cannot be derived with conventional ultrasound techniques. Clinically, tissue elasticity is known to be associated with pathological condition and with the ability to image these features in vivo; elasticity imaging methods may prove to be invaluable tools for the diagnosis and/or monitoring of disease. This review focuses on ultrasound-based elasticity imaging methods that generate an acoustic radiation force to induce tissue displacements. These methods can be performed noninvasively during routine exams to provide either qualitative or quantitative metrics of tissue elasticity. A brief overview of soft tissue mechanics relevant to elasticity imaging is provided, including a derivation of acoustic radiation force, and an overview of the various acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging methods.
Figures



References
-
- Adams F. The Genuine Works of Hippocrates. William Wood and Company; 1891.
-
- Tohno E, Cosgrove DO, Sloane JP. Ultrasound diagnosis of breast diseases. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc.; 1994.
-
- Wolfe JN. Xeroradiography of the breast. Springfield, IL: Thomas; 1972.
-
- Bassett L, Gold R, Kimme-Smith C. Hand-held and automated breast ultrasound. Thorafore, NJ: Slack Inc.; 1986.
-
- Donegan WL, Spratt JS. Cancer of the breast. Philadelphia: Suanders; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

