Effect of duloxetine on pain, function, and quality of life among patients with chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 23549581
- PMCID: PMC3912515
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.2813
Effect of duloxetine on pain, function, and quality of life among patients with chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Importance: There are no known effective treatments for painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Objective: To determine the effect of duloxetine, 60 mg daily, on average pain severity.
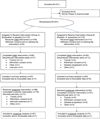
Design, setting, and patients: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial at 8 National Cancer Institute (NCI)-funded cooperative research networks that enrolled 231 patients who were 25 years or older being treated at community and academic settings between April 2008 and March 2011. Study follow-up was completed July 2012. Stratified by chemotherapeutic drug and comorbid pain risk, patients were randomized to receive either duloxetine followed by placebo or placebo followed by duloxetine. Eligibility required that patients have grade 1 or higher sensory neuropathy according to the NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events and at least 4 on a scale of 0 to 10, representing average chemotherapy-induced pain, after paclitaxel, other taxane, or oxaliplatin treatment.
Interventions: The initial treatment consisted of taking 1 capsule daily of either 30 mg of duloxetine or placebo for the first week and 2 capsules of either 30 mg of duloxetine or placebo daily for 4 additional weeks.
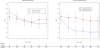
Main outcome measures: The primary hypothesis was that duloxetine would be more effective than placebo in decreasing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain severity was assessed using the Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form "average pain" item with 0 representing no pain and 10 representing as bad as can be imagined.
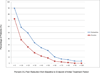
Results: Individuals receiving duloxetine as their initial 5-week treatment reported a mean decrease in average pain of 1.06 (95% CI, 0.72-1.40) vs 0.34 (95% CI, 0.01-0.66) among those who received placebo (P = .003; effect size, 0.513). The observed mean difference in the average pain score between duloxetine and placebo was 0.73 (95% CI, 0.26-1.20). Fifty-nine percent of those initially receiving duloxetine vs 38% of those initially receiving placebo reported decreased pain of any amount.
Conclusion and relevance: Among patients with painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, the use of duloxetine compared with placebo for 5 weeks resulted in a greater reduction in pain.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00489411.
Figures

Comment in
-
Therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.JAMA. 2013 Aug 7;310(5):537-8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.7902. JAMA. 2013. PMID: 23925630 No abstract available.
-
Therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy--in reply.JAMA. 2013 Aug 7;310(5):538. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.7905. JAMA. 2013. PMID: 23925632 No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith EM, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL. The reliability and validity of a modified total neuropathy score-reduced and neuropathic pain severity items when used to measure chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving taxanes and platinums. Cancer Nurs. 2010;33(3):173–183. - PubMed
-
- Kautio AL, Haanpaa M, Kautiainen H, Kalso E, Saarto T. Burden of chemotherapy-induced neuropathy--a cross-sectional study. Support Care Cancer. 2011;19(12):1991–1996. - PubMed
-
- Smith EML, Bakitas MA, Homel P, et al. Preliminary assessment of a neuropathic pain treatment and referral algorithm for patients with cancer. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2011;42(6):822–838. - PubMed
-
- Bakitas MA. Background noise: The experience of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Nurs Res. 2007;56(5):323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

