Macular and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in children with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia
- PMID: 23550031
- PMCID: PMC3580257
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.01.18
Macular and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in children with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia
Abstract
Aim: To compare the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness and macular thickness in the amblyopic eye with that in the sound eye of children with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia using optical coherence tomography (OCT).
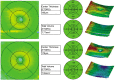
Methods: A prospective, nonrandom, intraindividual comparative cohort study includes 72 children with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia in a single center. Macular thickness, macular foveola thickness, and peripapillary RNFL thickness were compared between the amblyopia eyes and the contralateral sound eyes.
Results: There were 38 male and 34 female patients, with a mean age as 9.7±1.9 years (range, 5-16 years). Hyperopic was +3.62±1.16D (range +2.00D to +6.50D) in the amblyopic eyes, which was significantly higher in the control eyes with +0.76±0.90D (range 0D to +2.00D) (P < 0.01). The mean peripapillary RNFL thickness was 113.9±7.2µm and 109.2±6.9µm in the amblyopic eye and the normal eye, respectively, reaching statistical significance (P = 0.02). The mean macular foveola thickness was significantly thicker in the amblyopic eyes than the contralateral sound eyes (181.4±14.2µm vs 175.2±13.3µm, P < 0.01), but the 1mm, 3mm or 6mm macular thickness central macular thickness was not significantly different. Degree of anisometropia in the contralateral eyes was not significantly correlated with differences of peripapillary RNFL, macular foveola thickness or central macular thickness.
Conclusion: Eyes with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia are found thicker macular foveola and peripapillary RNFL than the contralateral eyes in children.
Keywords: children; hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia; macular thickness; optical coherence tomography; retinal nerve fiber thickness.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thicknesses of macular retinal layer and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer in patients with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005 Mar;19(1):62-7. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2005.19.1.62. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15929489
-
The assessment of anterior and posterior ocular structures in hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Apr 25;21:1181-8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893979. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 25910432 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the retinal ganglion cell and choroidal thickness in young Turkish adults with hyperopic anisometropic amblyopia.Int Ophthalmol. 2016 Aug;36(4):515-20. doi: 10.1007/s10792-015-0157-4. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Int Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26627688
-
[Macular thickness in unilateral amblyopia as measured by optical coherence tomography: a meta analysis].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jul;50(7):504-10. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25312459 Review. Chinese.
-
Levodopa Plus Occlusion Therapy versus Occlusion Therapy Alone for Children with Anisometropic Amblyopia.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2019 Oct 24;14(4):457-464. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v14i4.5451. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2019. PMID: 31875101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The association between macular thickness and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Chinese children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Feb;94(8):e567. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000567. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25715254 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in macular ultrastructural morphology in unilateral anisometropic amblyopia.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Aug 15;11(8):5086-5095. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31497224 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomographic Angiography in Children With Amblyopia.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Oct 1;135(10):1086-1091. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.3423. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28910439 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in anisometropic amblyopia via optic coherence tomography.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019 Oct;257(10):2103-2110. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04402-2. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31270595
-
CAN Optical Coherence Tomography redefine amblyopia?Rom J Ophthalmol. 2017 Apr-Jun;61(2):95-100. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2017.18. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29450380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Von Noorden GK. Classification of amblyopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967;63(2):238–244. - PubMed
-
- Von Noorden GK. Histological studies of the visual system in monkeys with experimental amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973;12(10):727–738. - PubMed
-
- Von Noorden GK, Middleditch PR. Histology of the monkey lateral geniculate nucleus after unilateral lid closure and experimental strabismus: further observations. Invest Ophthalmol. 1975;14(9):674–683. - PubMed
-
- Yen MY, Cheng CY, Wang AG. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in unilateral amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45(7):2224–2230. - PubMed
-
- Huynh SC, Wang XY, Rochtchina E, Mitchell P. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in a population of 6-year-old children: findings by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(9):1583–1592. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
