Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States
- PMID: 23551121
- PMCID: PMC3708105
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.12098
Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States
Abstract
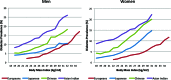
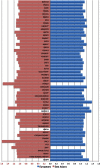
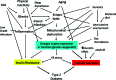
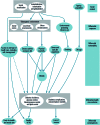
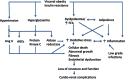
There is an epidemic of diabetes in Asia. Type 2 diabetes develops in East Asian patients at a lower mean body mass index (BMI) compared with those of European descent. At any given BMI, East Asians have a greater amount of body fat and a tendency to visceral adiposity. In Asian patients, diabetes develops at a younger age and is characterized by early β cell dysfunction in the setting of insulin resistance, with many requiring early insulin treatment. The increasing proportion of young-onset and childhood type 2 diabetes is posing a particular threat, with these patients being at increased risk of developing diabetic complications. East Asian patients with type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of developing renal complications than Europeans and, with regard to cardiovascular complications, a predisposition for developing strokes. In addition to cardiovascular-renal disease, cancer is emerging as the other main cause of mortality. While more research is needed to explain these interethnic differences, urgent and concerted actions are needed to raise awareness, facilitate early diagnosis, and encourage preventive strategies to combat these growing disease burdens.
© 2013 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. 5th ed. Belgium: IDF; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006;368:1681–1688. - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301:2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran A, Ma RC, Snehalatha C. Diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2010;375:408–418. - PubMed
-
- Ma RC, Tong PC. “Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes”. In: Holt R, Goldstein B, Flyvbjerg A, Cockram CS, editors. Textbook of Diabetes. 4th ed. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010. pp. 45–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

