n-3 and n-6 Fatty acids are independently associated with lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 23551952
- PMCID: PMC4060439
- DOI: 10.1017/S0007114513000949
n-3 and n-6 Fatty acids are independently associated with lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is an independent risk factor for CVD and has been proposed as a marker of vascular inflammation. Polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids (FA) and several n-6 FA are known to suppress inflammation and may influence Lp-PLA2 mass and activity. The associations of n-3 and n-6 plasma FA with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were analysed using linear regression analysis in 2246 participants of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis; statistical adjustments were made to control for body mass, inflammation, lipids, diabetes, and additional clinical and demographic factors. Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were significantly lower in participants with the higher n-3 FA EPA (β = - 4·72, P< 0·001; β = - 1·53; P= 0·023) and DHA levels (β = - 4·47, β = - 1·87; both P< 0·001). Those in the highest quintiles of plasma EPA and DHA showed 12·71 and 19·15 ng/ml lower Lp-PLA2 mass and 5·7 and 8·90 nmol/min per ml lower Lp-PLA2 activity than those in the first quintiles, respectively. In addition, lower Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were associated with higher levels of n-6 arachidonic acid (β = - 1·63, β = - 1·30; both P< 0·001), while γ-linolenic acid was negatively associated with activity (β = - 27·7, P= 0·027). Lp-PLA2 mass was significantly higher in participants with greater plasma levels of n-6 linoleic (β = 0·828, P= 0·011) and dihomo-γ-linolenic acids (β = 4·17, P= 0·002). Based on their independent associations with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity, certain n-3 and n-6 FA may have additional influences on CVD risk. Intervention studies are warranted to assess whether these macronutrients may directly influence Lp-PLA2 expression or activity.
Figures
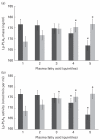
 ). Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. Values were adjusted for age, sex, race, education, field centre, smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin. * Mean values were significantly different from those of quintile 1 (P<0·05).
). Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. Values were adjusted for age, sex, race, education, field centre, smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin. * Mean values were significantly different from those of quintile 1 (P<0·05).
References
-
- Gazi I, Lourida ES, Filippatos T, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity is a marker of small dense LDL particles in human plasma. Clin Chem. 2005;51:2264–2273. - PubMed
-
- Serruys PW, García-García HM, Buszman P, et al. Integrated biomarker and imaging study-2 investigators. Effects of the direct lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitor darapladib on human coronary atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation. 2008;118:1172–1182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

