Three-dimensional architecture of tick-borne encephalitis virus replication sites and trafficking of the replicated RNA
- PMID: 23552408
- PMCID: PMC3648123
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03456-12
Three-dimensional architecture of tick-borne encephalitis virus replication sites and trafficking of the replicated RNA
Abstract
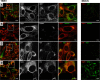
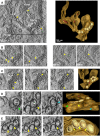
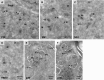
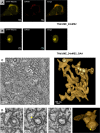
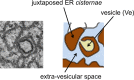
Flavivirus replication is accompanied by the rearrangement of cellular membranes that may facilitate viral genome replication and protect viral components from host cell responses. The topological organization of viral replication sites and the fate of replicated viral RNA are not fully understood. We exploited electron microscopy to map the organization of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) replication compartments in infected cells and in cells transfected with a replicon. Under both conditions, 80-nm vesicles were seen within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that in infected cells also contained virions. By electron tomography, the vesicles appeared as invaginations of the ER membrane, displaying a pore that could enable release of newly synthesized viral RNA into the cytoplasm. To track the fate of TBEV RNA, we took advantage of our recently developed method of viral RNA fluorescent tagging for live-cell imaging combined with bleaching techniques. TBEV RNA was found outside virus-induced vesicles either associated to ER membranes or free to move within a defined area of juxtaposed ER cisternae. From our results, we propose a biologically relevant model of the possible topological organization of flavivirus replication compartments composed of replication vesicles and a confined extravesicular space where replicated viral RNA is retained. Hence, TBEV modifies the ER membrane architecture to provide a protected environment for viral replication and for the maintenance of newly replicated RNA available for subsequent steps of the virus life cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Model System for the Formation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication Compartments without Viral RNA Replication.J Virol. 2019 Aug 28;93(18):e00292-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00292-19. Print 2019 Sep 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31243132 Free PMC article.
-
Tick-borne encephalitis virus delays interferon induction and hides its double-stranded RNA in intracellular membrane vesicles.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8470-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00176-10. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20554782 Free PMC article.
-
The ACBD3 protein coordinates ER-Golgi contacts to enable productive TBEV infection.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0222424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02224-24. Epub 2025 Apr 10. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40207930 Free PMC article.
-
Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Structural View.Viruses. 2018 Jun 28;10(7):350. doi: 10.3390/v10070350. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29958443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steps of the tick-borne encephalitis virus replication cycle that affect neuropathogenesis.Virus Res. 2005 Aug;111(2):161-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.007. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15871909 Review.
Cited by
-
Compartmentalized replication organelle of flavivirus at the ER and the factors involved.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(11):4939-4954. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03834-6. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33846827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multiples Fates of the Flavivirus RNA Genome During Pathogenesis.Front Genet. 2018 Dec 4;9:595. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00595. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30564270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Host Cell Secretory Machinery in Zika Virus Life Cycle.Viruses. 2018 Oct 15;10(10):559. doi: 10.3390/v10100559. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30326556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Mediated Immune Responses and Immunopathogenesis of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus-Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 26;9:2174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02174. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Proteins in Flavivirus Replication and Assembly Complexes.Pathogens. 2019 Sep 12;8(3):148. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8030148. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31547236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gritsun TS, Lashkevich VA, Gould EA. 2003. Tick-borne encephalitis. Antiviral Res. 57:129–146 - PubMed
-
- Lindquist L, Vapalahti O. 2008. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 371:1861–1871 - PubMed
-
- Mansfield KL, Johnson N, Phipps LP, Stephenson JR, Fooks AR, Solomon T. 2009. Tick-borne encephalitis virus—a review of an emerging zoonosis. J. Gen. Virol. 90:1781–1794 - PubMed
-
- Gubler DJ, Kuno G, Markoff L. 2007. Flaviviruses, p 1153–1252 In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA. (ed), Fields virology, fifth ed Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
-
- Lindenbach BD, Thiel HJ, Rice CM. 2007. Flaviviridae: the viruses and their replication, p 1101–1152 In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA. (ed), Fields virology, fifth ed Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

