IKKβ-I-κBɛ-c-Rel/p50: a new axis of NF-κB activation in lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 23552605
- PMCID: PMC3412642
- DOI: 10.1038/oncsis.2012.8
IKKβ-I-κBɛ-c-Rel/p50: a new axis of NF-κB activation in lung epithelial cells
Abstract
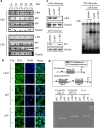
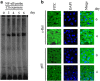
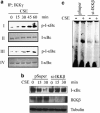
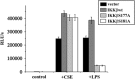
Cigarette smoke (CS), a major risk factor for developing lung cancer, is known to activate transcriptional activator nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). However, the underlying mechanism of this activation remains unclear because of conflicting reports. As NF-κB has a pivotal role in the generation and maintenance of malignancies, efforts were targeted towards understanding its activation mechanism using both ex vivo and in vivo studies. The results show that CS-induced NF-κB activation mechanism is different from that of other pro-inflammatory signals such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The NF-κB dimer that translocates to the nucleus upon stimulation with CS is predominantly composed of c-Rel/p50 and this translocation involves degradation of I-κBɛ and not I-κBα. This degradation of I-κBɛ depends on IKKβ activity, which preferentially targets I-κBɛ. Consistently, CS-activated form of IKKβ was found to be different from that involved in LPS activation as neither Ser177 nor Ser181 of IKKβ is crucial for CS-induced NF-κB activation. Thus, unlike other pro-inflammatory stimulations where p65 and I-κBα have a central role, the predominantly active signaling cascade in CS-induced NF-κB activation in the lung epithelial cells comprises of IKKβ-I-κBɛ-c-Rel/p50. Thus, this study uncovers a new axis of NF-κB activation wherein I-κBɛ and c-Rel have the central role.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin C forestalls cigarette smoke induced NF-κB activation in alveolar epithelial cells.Toxicol Lett. 2013 Jun 20;220(1):76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Toxicol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23615073
-
Alpha-melanocyte-related tripeptide, Lys-d-Pro-Val, ameliorates endotoxin-induced nuclear factor kappaB translocation and activation: evidence for involvement of an interleukin-1beta193-195 receptor antagonism in the alveolar epithelium.Biochem J. 2001 Apr 1;355(Pt 1):29-38. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3550029. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11256945 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of NF-{kappa}B1 (p50) augments cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema in mice: a critical role of p50 in chromatin remodeling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):L197-209. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00265.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19965984 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple redox regulation in NF-kappaB transcription factor activation.Biol Chem. 1997 Nov;378(11):1237-45. Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9426183 Review.
-
NF-kappaB dimers in the regulation of neuronal survival.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:351-62. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)85024-1. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19607980 Review.
Cited by
-
Disulfiram Protects Against Multiorgan Injuries and Cell Pyroptosis via Inhibiting GSDMD in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(15):e70707. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70707. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40801277 Free PMC article.
-
c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-κB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 9;5(10):e1455. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.417. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25299780 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the effects of vitamin C supplementation for pregnant smokers on the pulmonary function of their offspring.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Mar 7;24(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06377-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38454340 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation of Nuclear Factor-κΒ Expression Patterns in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132527. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147201 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pryor WA, Stone K.Oxidants in cigarette smoke. Radicals, hydrogen peroxide, peroxynitrate, and peroxynitrite Ann N Y Acad Sci 199368612–27.(discussion 27–28). - PubMed
-
- Orosz Z, Csiszar A, Labinskyy N, Smith K, Kaminski PM, Ferdinandy P, et al. Cigarette smoke-induced proinflammatory alterations in the endothelial phenotype: role of NAD(P)H oxidase activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292:H130–H139. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. The I-κB kinase - a bridge between inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2008;18:334–342. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa M, Kakemizu N, Ito T, Kudo M, Kaneko T, Suzuki M, et al. Superoxide mediates cigarette smoke-induced infiltration of neutrophils into the airways through nuclear factor-κB activation and IL-8 mRNA expression in guinea pigs in vivo. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;20:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Anto RJ, Mukhopadhyay A, Shishodia S, Gairola CG, Aggarwal BB. Cigarette smoke condensate activates nuclear transcription factor-κB through phosphorylation and degradation of I-κBα: correlation with induction of cyclooxygenase-2. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:1511–1518. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

