High circulating VEGF level predicts poor overall survival in lung cancer
- PMID: 23552871
- PMCID: PMC11824210
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-013-1425-1
High circulating VEGF level predicts poor overall survival in lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is considered as the best-validated key regulator of angiogenesis, while the prognostic role of circulating VEGF in lung cancer remains controversial. We conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic role of circulating VEGF.
Methods: Nineteen studies with a total number of 2,890 patients were analyzed in our meta-analysis. Hazard ratios (HRs) and their 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were used to quantify the predictive ability of circulating VEGF on survival.
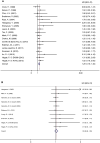
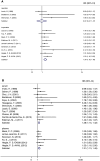
Results: The pooled HR of all 17 studies evaluating overall survival (OS) was 1.29 (95 % CI 1.19-1.40, p < 0.001), indicating high circulating VEGF predicted poor OS. When grouped by disease stages, the pooled HRs were 0.97 (95 % CI 0.47-1.47, p < 0.001) for operable stage and 1.34 (95 % CI 1.18-1.49, p < 0.001) for inoperable stage. The pooled HRs were 1.28 (95 % CI 1.15-1.42, p < 0.001) for serum and 1.31 (95 % CI 1.13-1.49, p < 0.001) for plasma, when categorized by blood sample. Meta-analysis of circulating VEGF related to progression-free survival (PFS) was performed in 7 studies, and the pooled HR was 1.03 (95 % CI 0.96-1.09).
Conclusions: Our results indicate that high level of circulating VEGF predicts poor OS in lung cancer, yet it does not predict poor PFS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- An SJ, Huang YS, Chen ZH, Su J, Yang Y, Chen JG, Yan HH, Lin QX, Yang JJ, Yang XN, Zhou Q, Zhang XC, Wu YL (2012) Posttreatment plasma VEGF levels may be associated with the overall survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy. Med Oncol 29(2):627–632. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9924-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brattstrom D, Bergqvist M, Larsson A, Holmertz J, Hesselius P, Rosenberg L, Brodin O, Wagenius G (1998) Basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in sera from non-small cell lung cancer patients. Anticancer Res 18(2A):1123–1127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

