Phase 2 study of dose-intense temozolomide in recurrent glioblastoma
- PMID: 23553268
- PMCID: PMC3688016
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/not040
Phase 2 study of dose-intense temozolomide in recurrent glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Among patients with glioblastoma (GBM) who progress on standard temozolomide, the optimal therapy is unknown. Resistance to temozolomide is partially mediated by O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT). Because MGMT may be depleted by prolonged temozolomide administration, dose-intense schedules may overcome resistance.
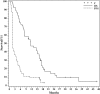
Methods: This was a multicenter, phase 2, single-arm study of temozolomide (75-100 mg/m(2)/day) for 21 days of each 28-day cycle. Patients had GBM in first recurrence after standard therapy. The primary end point was 6-month progression-free survival (PFS6).
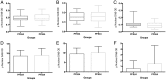
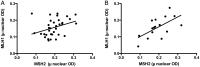
Results: Fifty-eight participants were accrued, 3 of whom were ineligible for analysis; one withdrew before response assessment. There were 33 men (61%), with a median age of 57 years (range, 25-79 years) and a median Karnofsky performance score of 90 (range, 60-100). Of 47 patients with MGMT methylation results, 36 (65%) had methylated tumors. There were 7 (13%) partial responses, and PFS6 was only 11%. Response and PFS did not depend on MGMT status; MSH2, MLH1, or ERCC1 expression; the number of prior temozolomide cycles; or the time off temozolomide. Treatment was well tolerated, with limited grade 3 neutropenia (n = 2) or thrombocytopenia (n = 2).
Conclusions: Dose-intense temozolomide on this schedule is safe in recurrent GBM. However, efficacy is marginal and predictive biomarkers are needed.
Keywords: MGMT promoter methylation; dose-intense temozolomide; recurrent glioblastoma.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492–507. - PubMed
-
- Stewart LA. Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet. 2002;359(9311):1011–1018. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, et al. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(28):4733–4740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

