Effectiveness of golimumab in clinical management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23553540
- PMCID: PMC3627033
- DOI: 10.1007/s40268-013-0010-z
Effectiveness of golimumab in clinical management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Limited data are available regarding the use of golimumab (100 mg) every 4 weeks, with or without methotrexate (MTX). The aim of this retrospective analysis was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of golimumab following usual clinical practice in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) according to the recommendations given in the Japanese package insert.
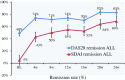
Patients and methods: Japanese RA patients with moderate-to-high disease activity, according to the 28-joint disease activity score based on C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) criteria, despite treatment with MTX or another biological agent, were enrolled. Patients were assigned to 50 mg golimumab plus MTX or 100 mg golimumab monotherapy every 4 weeks for 24 weeks. All patients were given MTX if it was not contraindicated. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving clinical remission (defined as a DAS28-CRP <2.3 or a simplified disease activity index [SDAI] score <3.3) at 24 weeks.
Results: Most patients received combined 50 mg golimumab plus MTX (41/43). In these patients, the primary endpoint, clinical remission, was attained in 83 % of patients according to DAS28-CRP criteria (p < 0.001) and 69 % according to SDAI criteria (p < 0.001) by week 24. Adverse events were reported in 11.6 % of patients receiving golimumab.
Conclusions: Golimumab (50 mg) plus MTX effectively reduced the signs and symptoms of RA and was generally well tolerated in patients with an inadequate response to MTX and other biological agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64(5):625–639. doi: 10.1002/acr.21641. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malottki K, Barton P, Tsourapas A, et al. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2011;15(14):1–278. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

