Noninvasive fetal genome sequencing: a primer
- PMID: 23553552
- PMCID: PMC3727971
- DOI: 10.1002/pd.4097
Noninvasive fetal genome sequencing: a primer
Abstract
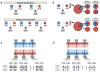
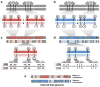
We recently demonstrated whole genome sequencing of a human fetus using only parental DNA samples and plasma from the pregnant mother. This proof-of-concept study demonstrated how samples obtained noninvasively in the first or second trimester can be analyzed to yield a highly accurate and substantially complete genetic profile of the fetus, including both inherited and de novo variation. Here, we revisit our original study from a clinical standpoint, provide an overview of the scientific approach, and describe opportunities and challenges along the path toward clinical adoption of noninvasive fetal whole genome sequencing.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. is a member of the scientific advisory board or serves as a consultant for Ariosa Diagnostics, Stratos Genomics, Good Start Genetics, and Adaptive Biotechnologies. A provisional patent application has been deposited for aspects of these methods (M.W.S., J.O.K., and J.S.; “Non-invasive whole genome sequencing of a human fetus”; 61/651,356)
Figures

References
-
- Merkatz IR, Nitowsky HM, Macri JN, Johnson WE. An association between low maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984;148:886–894. - PubMed
-
- ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 77: screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;109:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Lapaire O, Holzgreve W, Oosterwijk JC, Brinkhaus R, Bianchi DW. Georg Schmorl on Trophoblasts in the Maternal Circulation. Placenta. 2007;28:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Schröder J, De la Chapelle A. Fetal lymphocytes in the maternal blood. Blood. 1972;39:153–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

