DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) promotes lupus nephritis by activating the calcium pathway
- PMID: 23553627
- PMCID: PMC3650390
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.457218
DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) promotes lupus nephritis by activating the calcium pathway
Abstract
Background: Macrophage M2b polarization conferred by self-DNA immunization initiates and propagates lupus nephritis.
Results: Knockdown of DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) ameliorates SLE syndrome via blunting macrophage M2b polarization.
Conclusion: DAI functions as a DNA sensor in self-DNA-induced macrophage M2b polarization and lupus nephritis.
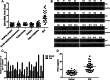
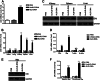
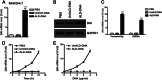
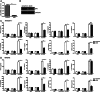
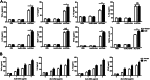
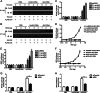
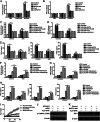
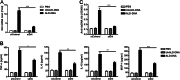
Significance: We disclose the mechanism by which self-DNA induces macrophage M2b polarization and lupus nephritis DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) functions as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor that activates the innate immune system. We previously found that activated lymphocyte-derived self-apoptotic DNA (ALD-DNA) immunization led to pathological macrophage activation and M2b polarization, which could initiate and propagate murine lupus nephritis. However, the specific DNA sensor(s) as well as underlying molecular mechanisms involved in ALD-DNA-induced macrophage M2b polarization in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease remains unknown. In this study, we reported that DAI expression was significantly increased in SLE patients as well as in lupus mice. Gain- and loss-of-function studies revealed that DAI was involved in ALD-DNA-induced macrophage activation and M2b polarization. Moreover, ALD-DNA notably induced dimerization/oligomerization of DAI and consequently activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) signaling pathways via calcium signaling, resulting in macrophage activation and M2b polarization. More importantly, blockade of DAI in vivo or selective knockdown of DAI in macrophages could ameliorate SLE syndrome via blunting macrophage M2b polarization and inhibiting inflammatory response in lupus mice. Our results suggest that DAI could function as a DNA sensor and a regulator in ALD-DNA-induced macrophage M2b polarization and lupus nephritis, providing the possible molecular mechanisms involved in ALD-DNA-induced macrophage M2b polarization in SLE disease and making DAI as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of SLE.
Keywords: Autoimmune Diseases; Calcium; DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1); DNA Sensor; Inflammation; Innate immunity; Lupus Nephritis; Macrophage Polarization; Macrophages; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Macrophage differentiation and polarization via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-ERK signaling pathway conferred by serum amyloid P component.J Immunol. 2011 Aug 15;187(4):1764-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002315. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21753147
-
Blockade of Notch1 signaling alleviates murine lupus via blunting macrophage activation and M2b polarization.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 1;184(11):6465-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904016. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20427764
-
Blockade of macrophage autophagy ameliorates activated lymphocytes-derived DNA induced murine lupus possibly via inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5):705-14. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25151985
-
Regulation of macrophage polarization by targeted metabolic reprogramming for the treatment of lupus nephritis.Mol Med. 2024 Jun 25;30(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00866-z. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38914953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Jun 8;2023:8821610. doi: 10.1155/2023/8821610. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37332618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Mitochondrial Nucleic Acid Sensing Pathways in Health and Patho-Physiology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 11;10:796066. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.796066. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35223833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Fragmented Self-DNA Is Involved in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 26;12:686121. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.686121. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34381477 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Strategies to Enhance the Efficacy of STING Activators in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 26;20:5429-5456. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S515893. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40308645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of treatment response in lupus nephritis using density of tubulointerstitial macrophage infiltration.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 13;15:1321507. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1321507. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38415246 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern recognition receptors as potential therapeutic targets in inflammatory rheumatic disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 May 15;17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0645-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25975607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Savill J., Dransfield I., Gregory C., Haslett C. (2002) A blast from the past. Clearance of apoptotic cells regulates immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 965–975 - PubMed
-
- Wen Z. K., Xu W., Xu L., Cao Q. H., Wang Y., Chu Y. W., Xiong S. D. (2007) DNA hypomethylation is crucial for apoptotic DNA to induce systemic lupus erythematosus-like autoimmune disease in SLE-non-susceptible mice. Rheumatology 46, 1796–1803 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

