Metabolomic profiling reveals a role for caspase-2 in lipoapoptosis
- PMID: 23553630
- PMCID: PMC3656301
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.437210
Metabolomic profiling reveals a role for caspase-2 in lipoapoptosis
Abstract
The accumulation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) in non-adipose tissues results in lipid-induced cytotoxicity (or lipoapoptosis). Lipoapoptosis has been proposed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of several metabolic diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. In this report, we demonstrate a novel role for caspase-2 as an initiator of lipoapoptosis. Using a metabolomics approach, we discovered that the activation of caspase-2, the initiator of apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts, is associated with an accumulation of LCFA metabolites. Metabolic treatments that blocked the buildup of LCFAs potently inhibited caspase-2 activation, whereas adding back an LCFA in this scenario restored caspase activation. Extending these findings to mammalian cells, we show that caspase-2 was engaged and activated in response to treatment with the saturated LCFA palmitate. Down-regulation of caspase-2 significantly impaired cell death induced by saturated LCFAs, suggesting that caspase-2 plays a pivotal role in lipid-induced cytotoxicity. Together, these findings reveal a previously unknown role for caspase-2 as an initiator caspase in lipoapoptosis and suggest that caspase-2 may be an attractive therapeutic target for inhibiting pathological lipid-induced apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase; Hepatocyte; Lipids; Metabolism.
Figures

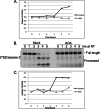
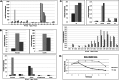
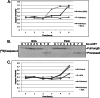
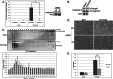

Similar articles
-
Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 28;281(17):12093-101. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510660200. Epub 2006 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16505490
-
Saturated free fatty acids induce cholangiocyte lipoapoptosis.Hepatology. 2014 Dec;60(6):1942-56. doi: 10.1002/hep.27175. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24753158 Free PMC article.
-
Death receptor 5 signaling promotes hepatocyte lipoapoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 11;286(45):39336-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.280420. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21941003 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:124-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24362249 Review.
-
Mechanisms of lipoapoptosis: implications for human heart disease.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2002 Apr;12(3):134-8. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(02)00152-4. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2002. PMID: 12007739 Review.
Cited by
-
Caspase-2 deficiency enhances whole-body carbohydrate utilisation and prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 26;8(10):e3136. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.518. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29072701 Free PMC article.
-
miR-21 ablation and obeticholic acid ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Apr 13;8(4):e2748. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.172. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28406477 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Apoptosis Induction and Its Regulation by Fatty Acids in Pancreatic β-Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4285. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5805-5837. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03433-5. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37349620 Review.
-
Age-related proteostasis and metabolic alterations in Caspase-2-deficient mice.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jan 22;6(1):e1615. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.567. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25611376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frayn K. N. (2002) Adipose tissue as a buffer for daily lipid flux. Diabetologia 45, 1201–1210 - PubMed
-
- Lewis G. F., Carpentier A., Adeli K., Giacca A. (2002) Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 23, 201–229 - PubMed
-
- Kusminski C. M., Shetty S., Orci L., Unger R. H., Scherer P. E. (2009) Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis 14, 1484–1495 - PubMed
-
- Unger R. H., Clark G. O., Scherer P. E., Orci L. (2010) Lipid homeostasis, lipotoxicity and the metabolic syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1801, 209–214 - PubMed
-
- Listenberger L. L., Schaffer J. E. (2002) Mechanisms of lipoapoptosis: implications for human heart disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 12, 134–138 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

