Membrane phospholipid bilayer as a determinant of monoacylglycerol lipase kinetic profile and conformational repertoire
- PMID: 23553709
- PMCID: PMC3690717
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2257
Membrane phospholipid bilayer as a determinant of monoacylglycerol lipase kinetic profile and conformational repertoire
Abstract
The membrane-associated serine hydrolase, monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), is a well-recognized therapeutic target that regulates endocannabinoid signaling. Crystallographic studies, while providing structural information about static MGL states, offer no direct experimental insight into the impact of MGL's membrane association upon its structure-function landscape. We report application of phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs as biomembrane models with which to evaluate the effect of a membrane system on the catalytic properties and conformational dynamics of human MGL (hMGL). Anionic and charge-neutral phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs enhanced hMGL's kinetic properties [apparent maximum velocity (Vmax) and substrate affinity (Km)]. Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry (HX MS) was used as a conformational analysis method to profile experimentally the extent of hMGL-nanodisc interaction and its impact upon hMGL structure. We provide evidence that significant regions of hMGL lid-domain helix α4 and neighboring helix α6 interact with the nanodisc phospholipid bilayer, anchoring hMGL in a more open conformation to facilitate ligand access to the enzyme's substrate-binding channel. Covalent modification of membrane-associated hMGL by the irreversible carbamate inhibitor, AM6580, shielded the active site region, but did not increase solvent exposure of the lid domain, suggesting that the inactive, carbamylated enzyme remains intact and membrane associated. Molecular dynamics simulations generated conformational models congruent with the open, membrane-associated topology of active and inhibited, covalently-modified hMGL. Our data indicate that hMGL interaction with a phospholipid membrane bilayer induces regional changes in the enzyme's conformation that favor its recruiting lipophilic substrate/inhibitor from membrane stores to the active site via the lid, resulting in enhanced hMGL catalytic activity and substrate affinity.
© 2013 The Protein Society.
Figures
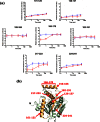
 ) or presence (red lines,
) or presence (red lines,  ) of POPC/POPG bilayer nanodiscs. The maximum amount of deuterium incorporation possible for each respective peptide is designated on the y-axis of each kinetic plot. Data were obtained through peptide level HX MS analysis of hMGL. The error of peptide HX MS mesurements with this experimental setup was ±0.50 Da, as determined by replicate analysis of peptide standards in prior HX MS work with this instrumentation., (b) The hMGL peptides for which deuterium uptake curves are presented in panel (a), above, are highlighted (orange) in the wild-type hMGL structure representation derived from PDB ID: 3JW8.26 Residue designations in red type correspond to 6-His-hMGL.
) of POPC/POPG bilayer nanodiscs. The maximum amount of deuterium incorporation possible for each respective peptide is designated on the y-axis of each kinetic plot. Data were obtained through peptide level HX MS analysis of hMGL. The error of peptide HX MS mesurements with this experimental setup was ±0.50 Da, as determined by replicate analysis of peptide standards in prior HX MS work with this instrumentation., (b) The hMGL peptides for which deuterium uptake curves are presented in panel (a), above, are highlighted (orange) in the wild-type hMGL structure representation derived from PDB ID: 3JW8.26 Residue designations in red type correspond to 6-His-hMGL.
 ) or with (green lines,
) or with (green lines,  ) AM6580. The maximum amount of deuterium incorporation possible for each respective peptide is designated on the y-axis of each kinetic plot. Data were obtained through peptide-based HX MS analysis. The error of peptide HX MS mesurements with this experimental setup was ±0.50 Da, as determined by replicate analysis of peptide standards in prior HX MS work with this instrumentation., (c) Schematic depicting the docking of the AM6580-derived fluorenyl piprazine group covalently attached to hMGL active-site Ser122 (i.e., Ser129 for 6-His-hMGL) in a portion of the hMGL structure representation derived from PDB ID: 3JW8.26 Helix-α6 peptide 217–223 (orange) is shielded by the carbamylating-group modification at Ser122.
) AM6580. The maximum amount of deuterium incorporation possible for each respective peptide is designated on the y-axis of each kinetic plot. Data were obtained through peptide-based HX MS analysis. The error of peptide HX MS mesurements with this experimental setup was ±0.50 Da, as determined by replicate analysis of peptide standards in prior HX MS work with this instrumentation., (c) Schematic depicting the docking of the AM6580-derived fluorenyl piprazine group covalently attached to hMGL active-site Ser122 (i.e., Ser129 for 6-His-hMGL) in a portion of the hMGL structure representation derived from PDB ID: 3JW8.26 Helix-α6 peptide 217–223 (orange) is shielded by the carbamylating-group modification at Ser122.

Similar articles
-
Active-site inhibitors modulate the dynamic properties of human monoacylglycerol lipase: a hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry study.Biochemistry. 2013 Jul 23;52(29):5016-26. doi: 10.1021/bi400430k. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23795559 Free PMC article.
-
Identification by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of an active-site hydrogen-bond network in human monoacylglycerol lipase (hMGL): implications for hMGL dynamics, pharmacological inhibition, and catalytic mechanism.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Aug;6(8):1381-8. doi: 10.1039/c004515b. Epub 2010 May 12. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20464001 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Inter-residue Interactions as Determinants of Human Monoacylglycerol Lipase Catalytic Competency: A ROLE FOR GLOBAL CONFORMATIONAL CHANGES.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 5;291(6):2556-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.670257. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26555264 Free PMC article.
-
Monoglyceride lipase: Structure and inhibitors.Chem Phys Lipids. 2016 May;197:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Chem Phys Lipids. 2016. PMID: 26216043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of hydrated phospholipid bilayers.Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1996 Dec;33(6):431-47. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1996. PMID: 9219427 Review.
Cited by
-
Active-site inhibitors modulate the dynamic properties of human monoacylglycerol lipase: a hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry study.Biochemistry. 2013 Jul 23;52(29):5016-26. doi: 10.1021/bi400430k. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23795559 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Distal Mutations on the Structure, Dynamics and Catalysis of Human Monoacylglycerol Lipase.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 29;8(1):1719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19135-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29379013 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of hydrogen/deuterium exchange MS from 2012 to 2014.Anal Chem. 2015 Jan 6;87(1):99-118. doi: 10.1021/ac5040242. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25398026 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The Endocannabinoid Signaling System in the CNS: A Primer.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015;125:1-47. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26638763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication in bioanalytical studies with HDX MS: aim as high as possible.Bioanalysis. 2015;7(9):1065-7. doi: 10.4155/bio.15.46. Bioanalysis. 2015. PMID: 26039804 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dinh TP, Kathuria S, Piomelli D. RNA interference suggests a primary role for monoacylglycerol lipase in the degradation of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:1260–1264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

