Serum arginase, a biomarker of treatment efficacy in human African trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 23554207
- PMCID: PMC3697696
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03371-12
Serum arginase, a biomarker of treatment efficacy in human African trypanosomiasis
Abstract
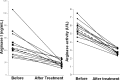
Arginase serum levels were increased in human African trypanosomiasis patients and returned to control values after treatment. Arginase hydrolyzes l-arginine to l-ornithine, which is essential for parasite growth. Moreover, l-arginine depletion impairs immune functions. Arginase may be considered as a biomarker for treatment efficacy.
Figures

References
-
- Van Meirvenne N, Le Ray D. 1985. Diagnosis of African and American trypanosomiasis. Br. Med. Bull. 41:156–161 - PubMed
-
- Vincendeau P, Bouteille B. 2006. Immunology and immunopathology of African trypanosomiasis. Ann. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 78:645–665 - PubMed
-
- Grohmann U, Bronte V. 2010. Control of immune response by amino acid metabolism. Immunol. Rev. 236:243–264 - PubMed
-
- Fairlamb AH, Cerami A. 1992. Metabolism and functions of trypanothione in the Kinetoplastida. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 46:695–729 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

