Prediction of candidate small non-coding RNAs in Agrobacterium by computational analysis
- PMID: 23554609
- PMCID: PMC3596533
- DOI: 10.1016/S1674-8301(10)60006-1
Prediction of candidate small non-coding RNAs in Agrobacterium by computational analysis
Abstract
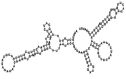
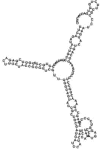
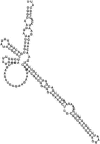
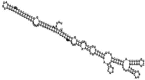
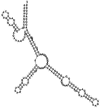
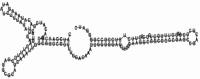
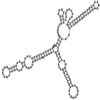
Small non-coding RNAs with important regulatory roles are not confined to eukaryotes. Recent work has uncovered a growing number of bacterial small RNAs (sRNAs), some of which have been shown to regulate critical cellular processes. Computational approaches, in combination with molecular experiments, have played an important role in the identification of these sRNAs. At present, there is no information on the presence of small non-coding RNAs and their genes in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens genome. To identify potential sRNAs in this important bacterium, deep sequencing of the short RNA populations isolated from Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 was carried out. From a data set of more than 10,000 short sequences, 16 candidate sRNAs have been tentatively identified based on computational analysis. All of these candidates can form stem-loop structures by RNA folding predictions and the majority of the secondary structures are rich in GC base pairs. Some are followed by a short stretch of U residues, indicative of a rho-independent transcription terminator, whereas some of the short RNAs are found in the stem region of the hairpin, indicative of eukaryotic-like sRNAs. Experimental strategies will need to be used to verify these candidates. The study of an expanded list of candidate sRNAs in Agrobacterium will allow a more complete understanding of the range of roles played by regulatory RNAs in prokaryotes.
Keywords: Agrobacterium tumefaciens genome; small RNAs; small non-coding RNAs; solexa sequencing technology.
Figures








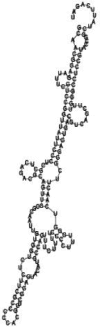

References
-
- Gottesman S. Micros for microbes:non-coding regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Trends Genet. 2005;21:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Livny J, Waldor MK. Identification of small RNAs in diverse bacterial species. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni RV, Kulkarni PR. Computational approaches for the discovery of bacterial small RNAs. Methods. 2007;43:131–9. - PubMed
-
- Rivas E, Klein RJ, Jones TA, Eddy SR. Computational identification of non-coding RNAs in E. coli by comparative genomics. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1369–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

