mRNA profiles of cytokine receptors in unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria
- PMID: 23554682
- PMCID: PMC3596706
- DOI: 10.1016/S1674-8301(11)60018-3
mRNA profiles of cytokine receptors in unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria
Abstract
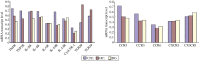
This present study was aimed to investigate the roles of the receptors of Th1/Th2 cytokines and chemokines in the pathogenesis of chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU). Thirty patients with CIU, 30 patients with dermographism and 30 healthy controls were randomly enrolled. Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) was used to analyze the mRNA of cytokine receptors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The mRNA levels of tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR), interferon-γ receptor (IFN-γR), and interleukin-10 receptor (IL-10R) were statistically increased in the CIU group (P < 0.05), while IL-2R, IL-4R, IL-6R, and IL-13R showed no significant differences between the CIU and other groups. The mRNA levels of CCR3 and CCR6 were statistically increased in the CIU group (P < 0.05). The toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) mRNA level was significantly lower in the CIU group than the healthy control group (P < 0.05). These findings indicate that the regulation of mRNA of TNFR, IFN-γR, IL-10R, CCR3, CCR6 and TLR2 may be involved in the pathogenesis of CIU.
Keywords: chemokine; cytokine; receptor; urticaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- DeMarco PJ. Chronic idiopathic Urticaria. Northeast Florida Medicine. 2008;59:15–7.
-
- Bansal AS, Hayman GR. Graves disease associated with chronic idiopathic urticaria: 2 case Reports. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009;19:54–6. - PubMed
-
- Sabroe RA, Fiebiger E, Francis DM, Maurer D, Seed PT, Grattan CE, et al. Classification of anti-FcϵRI and anti-IgE autoantibodies in chronic idiopathic urticaria and correlation with disease severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:492–9. - PubMed
-
- Ying S, Kikuchi Y, Meng Q, Kay AB, Kaplan AP. TH1/TH2 cytokines and inflammatory cells in skin biopsy specimens from patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria: Comparison with the allergeninduced late-phase cutaneous reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:694–700. - PubMed
-
- Konstantinou GN, Asero R, Maurer M, Sabroe RA, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Grattan CEH. EAACI/GA2LEN task force consensus report: the autologous serum skin test in urticaria. Allergy. 2009;64:1256–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

