Cardioprotective activity of alcoholic extract of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers in calcium chloride-induced cardiac arrhythmia in rats
- PMID: 23554702
- PMCID: PMC3597064
- DOI: 10.1016/S1674-8301(11)60038-9
Cardioprotective activity of alcoholic extract of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers in calcium chloride-induced cardiac arrhythmia in rats
Abstract
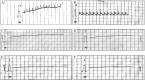
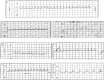
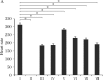
The present study investigated the antiarrhythmic activity of alcoholic extract of Tinospora cordifolia (T. cordifolia) in CaCl2 induced arrhythmia. CaCl2 (25 mg/kg) was administered by intravenous infusion (iv) to produce arrhythmia in rats. The animals were then treated with T. cordifolia extract (150, 250, and 450 mg/kg) and verapamil (5 mg/kg,iv). Lead II electrocardiogram was monitored. Plasma calcium, sodium and potassium levels were measured. In CaCl2 induced arrhythmia, heart rate was decreased by 41.10%, T. cordifolia at 150, 300, and 450 mg/kg decreased the heart rate by 26.30%, 29.16%, and 38.29%, respectively, and verapamil reduced the heart rate by 9.70% compared to the normal group. The PQRST waves were normalized and atrial and ventricular fibrillation was controlled in rats treated with verapamil and T. cordifolia. CaCl2 increased calcium and sodium levels and decreased potassium levels in blood. T. cordifolia dose-dependently decreased calcium and sodium levels and increased potassium levels. Hence, T. cordifolia can be used in antiarrhythmic clinical settings and beneficial in atrial and ventricular fibrillation and flutter and may be indicated in ventricular tachyarrhythmia.
Keywords: Tinospora cordifolia; arrhythmia; cardioprotection..
Conflict of interest statement
These authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roden DM. Antiarrhythmie Drugs. In: Laurence LB, Lazo JS, Parker KL, editors. Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmcological Basis of Thaerapeutics. 11th edition. New York: McGraw Hill; 2006. pp. 899–932.
-
- Thireau J, Pasquié JL, Martel E, Le Guennec JY, Richard S. New drugs vs. old concepts: A fresh look at antiarrhythmics. Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Mar 21; [Epub ahead of print], PMID: 21420430. - PubMed
-
- Nadkarni AK. Indian meteria medica. 3rd Revised edition. Bombay: 1954. Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.)Miers; p. 1221.
-
- Chopra RN, Chopra IC, Honda KL, Kapur LD. Indigenous drugs of India. 2nd edition. Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Dhar and Sons; Calcutta: 1958. Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Hook. f. (Guduchi) pp. 426–7.
-
- Atal CK, Sharma ML, Kaul A, Khajuria A. Immunomodulatory effects of NIM-76, a volatile fraction from Neem oil. J Ethnopharmacol. 1986;18:133–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

