Telmisartan prevents high-fat diet-induced hypertension and decreases perirenal fat in rats
- PMID: 23554752
- PMCID: PMC3596072
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.26.20120013
Telmisartan prevents high-fat diet-induced hypertension and decreases perirenal fat in rats
Abstract
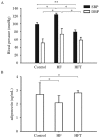
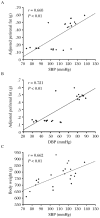
We sought to investigate the effects of telmisartan on high-fat diet-induced hypertension and to explore the possible underlying mechanisms. Rats receiving high-fat diet were randomly divided into two groups, the telmisartan group (n = 9) and the high-fat diet group (n = 10). The control group consisted of age-matched rats on a regular diet (n = 10). At the end of the treatment, the body weight, blood pressure, insulin sensitivity and serum adiponectin levels of all rats were examined, and their visceral fat was extracted and weighed. Our results showed that telmisartan improved insulin resistance and dyslipidemia and increased serum adiponectin levels. Telmisartan also lowered both systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, and decreased the accumulation of perirenal fat associated with high-fat diet. Furthermore, telmisartan increased adiponectin mRNA expression in the perirenal fat. Correlation analysis showed that both systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were positively correlated with perirenal fat. These effects of telmisartan may be mediated through decreases in perirenal fat and contributed to the improvement of perirenal fat function. Our findings suggested a strong link between perirenal fat and high-fat diet-induced hypertension, and identified telmisartan as a potential drug for the treatment of obesity-related hypertension.
Keywords: adiponectin; high-fat diet; hypertension; perirenal fat; telmisartan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nichols M, de Silva-Sanigorski A, Cleary J, Goldfeld S, Colahan A, Swinburn B. Decreasing trends in overweight and obesity among an Australian population of preschool children. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011;35:916–24. - PubMed
-
- Aneja A, El-Atat F, McFarlane SI, Sowers JR. Hypertension and obesity. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:169–205. - PubMed
-
- Sironi AM, Pingitore A, Ghione S, De Marchi D, Scattini B, Positano V, et al. Early hypertension is associated with reduced regional cardiac function, insulin resistance, epicardial, and visceral fat. Hypertension. 2008;51:282–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

