Ginkgo biloba leaf extract improves the cognitive abilities of rats with D-galactose induced dementia
- PMID: 23554791
- PMCID: PMC3596752
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.27.20120047
Ginkgo biloba leaf extract improves the cognitive abilities of rats with D-galactose induced dementia
Abstract
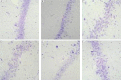
Standardized Ginkgo biloba leaf extract has been used in clinical trials for its beneficial effects on brain functions, particularly in dementia. Substantial experimental evidences indicated that Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGB) protected neuronal cells from a variety of insults. We investigated the effect of EGB on cognitive ability and protein kinase B (PKB) activity in hippocampal neuronal cells of dementia model rats. Rats received an intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose to induce dementia. Forty-eight Spraque-Dawley rats were randomly divided into six groups, including the control group, D-galactose group (Gal), low-dose EGB group (EGB-L), mid-dose EGB group (EGB-M), high-dose EGB group (EGB-H) and treatment group. The EGB-L, EGB-M and EGB-H groups were administered with EGB and D-galactose simultaneously. Y-maze, cresyl violet staining, TUNEL assays and immunohistochemistry staining were performed to detect learning and memory abilities, morphological changes in the hippocampus, neuronal apoptosis and the expressing level of phospho-PKB, respectively. Rats in the Gal group showed decreased abilities of learning and memory, and hippocampal pyramidal cell layer was damaged, while EGB administration improved learning and memory abilities. The Gal group exhibited many stained, condensed nuclei and micronuclei, either isolated or within the cytoplasm of cells (39.5±1.4). Apoptotic cells decreased in the groups of EGB-L (35.9±0.9), EGB-M (16.8±1.0) and EGB-H (10.1±0.8), and there were statistical significances compared with the Gal group. Immunoreactivity of phospho-PKB was localized diffusely throughout the cytosol of cells in all groups, while the immunoreactivity of the Gal group was weak. EGB significantly attenuated learning and memory impairment in a dose-dependent manner, while it could decrease the nmber of TUNEL-positive cells, and increase the activity of PKB. Our results demonstrated that EGB attenuated memory impairment and cell apoptosis in galactose-induced dementia model rats by activating PKB.
Keywords: D-galactose; Ginkgo biloba extract; apoptosis; cognitive ability; dementia model; protein kinase B (PKB).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cui X, Zuo P, Zhang Q, Li X, Hu Y, Long J, et al. Chronic systemic D-galactose exposure induces memory loss, neurodegeneration, and oxidative damage in mice: protective effects of R-alpha-lipoic acid. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84:647–54. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Liu G, Shi J, Zhang J. Coeloglossum viride var bracteatum extract attenuates D-galactose and NaNO2 induced memory impairment in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;104(1-2):250–6. - PubMed
-
- Kong WJ, Wang Y, Wang Q, Hu YJ, Han YC, Liu J. The relation between D-galactose injection and mitochondrial DNA 4834 bp deletion mutation. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41:628–34. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Li X, Cui X, Zuo P. D-galactose injured neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neurol Res. 2005;27:552–6. - PubMed
-
- DeFeudis FV, Drieu K. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) and CNS functions: basic studies and clinical applications [J] Curr Drug Targets. 2000;1:25–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

