Lactobacillus isolates from healthy volunteers exert immunomodulatory effects on activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 23554802
- PMCID: PMC3602869
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.27.20120074
Lactobacillus isolates from healthy volunteers exert immunomodulatory effects on activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
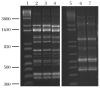
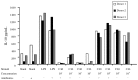
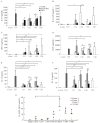
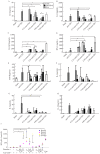
As probiotics in the gut, Lactobacilli are believed to play important roles in the development and maintenance of both the mucosal and systemic immune system of the host. This study was aimed to investigate the immuno-modulatory function of candiate lactobacilli on T cells. Lactobacilli were isolated from healthy human feces and the microbiological characteristics were identified by API 50 CHL and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assays. Anti-CD3 antibody activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were treated by viable, heat-killed lactobacilli and genomic DNA of lactobacilli, and cytokine profiles were tested by ELISA. Isolated lactobacilli C44 and C48 were identified as L. acidophilus and L. paracacei, which have properties of acid and bile tolerance and inhibitor effects on pathogens. Viable and heat-killed C44 and C48 induced low levels of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8) and high levels of IFN-γ and IL-12p70 in PBMCs. In anti-CD3 antibody activated PBMCs, viable and heat-killed C44 increased Th2 cytokine levels (IL-5, IL-6 and IL-10), and simultaneously enhanced Th1 responses by inducing IFN-γ and IL-12p70 production. Different from that of lactabacillus strains, their genomic DNA induced low levels of IL-12p70, IFN-γ and proinflammatory cytokines in PBMCs with or without anti-CD3 antibody activation. These results provided in vitro evidence that the genomic DNA of strains of C44 and C48, especially C44, induced weaker inflammation, and may be potentially applied for treating allergic diseases.
Keywords: Th1; Th2; cytokine; immuno-modulation; lactobacilli; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunomodulating Effects of Heat-Killed Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Healthy Dogs.Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 2;12(3):226. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030226. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40266946 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of strong interleukin-10 inducing lactic acid bacteria which down-regulate T helper type 2 cytokines.Clin Exp Allergy. 2005 Nov;35(11):1481-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02375.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16297146
-
Molecular identification of potential Th1/Th2 responses-modulating bacterial genes using suppression subtractive DNA hybridization.Immunobiology. 2014 Mar;219(3):208-17. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Immunobiology. 2014. PMID: 24192538
-
Heat-killed cells of lactobacilli skew the immune response toward T helper 1 polarization in mouse splenocytes and dendritic cell-treated T cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Dec 26;55(26):11080-6. doi: 10.1021/jf071786o. Epub 2007 Nov 27. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 18038979
-
Photoactivational cytokine-modulatory action of 8-methoxypsoralen plus ultraviolet A in lymphocytes, monocytes, and cutaneous T cell lymphoma cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Sep;941:185-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03722.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11594572 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacilli regulate Staphylococcus aureus 161:2-induced pro-inflammatory T-cell responses in vitro.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):e77893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077893. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205015 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Immune Functions by Limosilactobacillus reuteri KBL346: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):141. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010141. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203313 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Modulates Intestinal Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 31;22(1):362. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010362. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33396382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benefits and Inputs From Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins as Alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters During Food-Animal Production.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 11;10:57. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00057. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30804896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization Report of a joint FAO/WHO working group on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London, Ontario, Canada. 2002 Apr 30;
-
- Shida K, Takahashi R, Iwadate E, Takamizawa K, Yasui H, Sato T, et al. Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota suppresses serum immunoglobulin E and immunoglobulin G1 responses and systemic anaphylaxis in a food allergy model. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002;32:563–70. - PubMed
-
- Shirakawa T, Enomoto T, Shimazu S, Hopkin JM. The inverse association between tuberculin responses and atopic disorder. Science. 1997;275:77–9. - PubMed
-
- Prescott SL, Macaubas C, Smallacombe T, Holt BJ, Sly PD, Holt PG. Development of allergen-specific T-cell memory in atopic and normal children. Lancet. 1999;353:196–200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

