A randomized clinical trial of auricular point acupressure for chronic low back pain: a feasibility study
- PMID: 23554825
- PMCID: PMC3603381
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/196978
A randomized clinical trial of auricular point acupressure for chronic low back pain: a feasibility study
Abstract
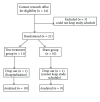
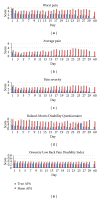
Objectives. This prospective, randomized clinical trial (RCT) was designed to investigate the feasibility and effects of a 4-week auricular point acupressure (APA) for chronic low back pain (CLBP). Methods. Participants were randomized to either true APA (true acupoints with taped seeds on the designated ear points for CLBP) or sham APA (sham acupoints with taped seeds but on different locations than those designated for CLBP). The duration of treatment was four weeks. Participants were assessed before treatment, weekly during treatment, and 1 month following treatment. Results. Participants in the true APA group who completed the 4-week APA treatment had a 70% reduction in worst pain intensity, a 75% reduction in overall pain intensity, and a 42% improvement in disability due to back pain from baseline assessment. The reductions of worst pain and overall pain intensity in the true APA group were statistically greater than participants in the sham group (P < 0.01) at the completion of a 4-week APA and 1 month followup. Discussion. The preliminary findings of this feasibility study showed a reduction in pain intensity and improvement in physical function suggesting that APA may be a promising treatment for patients with CLBP.
Figures
References
-
- Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and internationally. The Spine Journal. 2008;8(1):8–20. - PubMed
-
- Strine TW, Hootman JM. US national prevalence and correlates of low back and neck pain among adults. Arthritis Care and Research. 2007;57(4):656–665. - PubMed
-
- Haldeman S, Dagenais S. What have we learned about the evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain? The Spine Journal. 2008;8(1):266–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical