The effects of high-dose qinggan huoxue recipe on acute liver failure induced by d-galactosamine in rats
- PMID: 23554835
- PMCID: PMC3608312
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/905715
The effects of high-dose qinggan huoxue recipe on acute liver failure induced by d-galactosamine in rats
Abstract
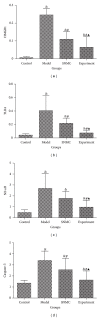
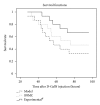
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe is a traditional Chinese medicine, which has been usually used to improve liver function in hepatitis. In order to investigate the effects of high-dose Qinggan Huoxue Recipe on acute liver failure and explore the potential mechanism, we had built acute liver failure models in rats by intraperitoneal injection of D-galactosamine (D-GalN). High-dose Qinggan Huoxue Recipe was delivered by gavage. After treatment, the blood alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), albumin (ALB), cholinesterase (CHE), and prothrombin time (PT) were determined. The pathological score of liver tissue was recorded. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunohistochemistry staining and fluorescence quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF- κ B), and Caspase-3 were performed. The survival curve was also depicted. Our results demonstrated that high-dose Qinggan Huoxue Recipe could significantly improve liver function and increase survival rates in rats with acute liver failure. These effects were supposed to be mediated by suppressing inflammatory reaction and apoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Taylor NJ, Nishtala A, Vijay GK, et al. Circulating neutrophil dysfunction in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2012 - PubMed
-
- Tan WF, Steadman RH, Farmer DG, et al. Pretransplant neurological presentation and severe posttransplant brain injury in patients with acute liver failure. Transplantation. 2012;94(7):768–774. - PubMed
-
- Ji G, Wang YQ, Cao CL. Clinical study on treatment of alcoholic liver disease by qinggan huoxue recipe. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004;24(1):13–16. - PubMed
-
- Chen JM, Wang L, Xing LJ. Regulatory effects of Qinggan Huoxue Recipe on matrix metalloproteinases of alcoholic liver fibrosis rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2011;31(11):1538–1544. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

