Genome and transcriptome analyses provide insight into the euryhaline adaptation mechanism of Crassostrea gigas
- PMID: 23554902
- PMCID: PMC3595286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058563
Genome and transcriptome analyses provide insight into the euryhaline adaptation mechanism of Crassostrea gigas
Abstract
Background: The Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, has developed special mechanisms to regulate its osmotic balance to adapt to fluctuations of salinities in coastal zones. To understand the oyster's euryhaline adaptation, we analyzed salt stress effectors metabolism pathways under different salinities (salt 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 40 for 7 days) using transcriptome data, physiology experiment and quantitative real-time PCR.
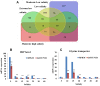
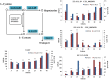
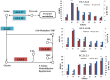
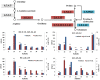
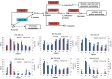
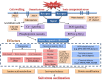
Results: Transcriptome data uncovered 189, 480, 207 and 80 marker genes for monitoring physiology status of oysters and the environment conditions. Three known salt stress effectors (involving ion channels, aquaporins and free amino acids) were examined. The analysis of ion channels and aquaporins indicated that 7 days long-term salt stress inhibited voltage-gated Na(+)/K(+) channel and aquaporin but increased calcium-activated K(+) channel and Ca(2+) channel. As the most important category of osmotic stress effector, we analyzed the oyster FAAs metabolism pathways (including taurine, glycine, alanine, beta-alanine, proline and arginine) and explained FAAs functional mechanism for oyster low salinity adaptation. FAAs metabolism key enzyme genes displayed expression differentiation in low salinity adapted individuals comparing with control which further indicated that FAAs played important roles for oyster salinity adaptation. A global metabolic pathway analysis (iPath) of oyster expanded genes displayed a co-expansion of FAAs metabolism in C. gigas compared with seven other species, suggesting oyster's powerful ability regarding FAAs metabolism, allowing it to adapt to fluctuating salinities, which may be one important mechanism underlying euryhaline adaption in oyster. Additionally, using transcriptome data analysis, we uncovered salt stress transduction networks in C. gigas.
Conclusions: Our results represented oyster salt stress effectors functional mechanisms under salt stress conditions and explained the expansion of FAAs metabolism pathways as the most important effectors for oyster euryhaline adaptation. This study was the first to explain oyster euryhaline adaptation at a genome-wide scale in C. gigas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hedgecock D, Gaffney PM, Goulletquer P, Guo XM, Reece K, et al. (2005) The case for sequencing the Pacific oyster genome. J Shellfish Res 24: 429–441.
-
- Brown JR (1988) Multivariate Analyses of the Role of Environmental Factors in Seasonal and Site Related Growth Variation in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas . Mar Ecol Prog Ser 45: 225–236.
-
- Bartol IK, Mann R, Luckenbach M (1999) Growth and mortality of oysters (Crassostrea virginica) on constructed intertidal reefs: effects of tidal height and substrate level. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 237: 157–184.
-
- Heilmayer O, Digialleonardo J, Qian LF, Roesijadi G (2008) Stress tolerance of a subtropical Crassostrea virginica population to the combined effects of temperature and salinity. Estuar Coast Shelf S 79: 179–185.
-
- Macinnes JR, Calabrese A (1979) Combined Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Copper on Embryos and Early Larvae of the American Oyster, Crassostrea virginica . Arch Environ Con Tox 8: 553–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

