The RAVEN toolbox and its use for generating a genome-scale metabolic model for Penicillium chrysogenum
- PMID: 23555215
- PMCID: PMC3605104
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002980
The RAVEN toolbox and its use for generating a genome-scale metabolic model for Penicillium chrysogenum
Abstract
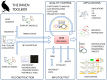
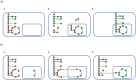
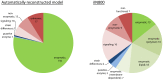
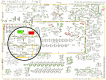
We present the RAVEN (Reconstruction, Analysis and Visualization of Metabolic Networks) Toolbox: a software suite that allows for semi-automated reconstruction of genome-scale models. It makes use of published models and/or the KEGG database, coupled with extensive gap-filling and quality control features. The software suite also contains methods for visualizing simulation results and omics data, as well as a range of methods for performing simulations and analyzing the results. The software is a useful tool for system-wide data analysis in a metabolic context and for streamlined reconstruction of metabolic networks based on protein homology. The RAVEN Toolbox workflow was applied in order to reconstruct a genome-scale metabolic model for the important microbial cell factory Penicillium chrysogenum Wisconsin54-1255. The model was validated in a bibliomic study of in total 440 references, and it comprises 1471 unique biochemical reactions and 1006 ORFs. It was then used to study the roles of ATP and NADPH in the biosynthesis of penicillin, and to identify potential metabolic engineering targets for maximization of penicillin production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Liu L, Agren R, Bordel S, Nielsen J (2010) Use of genome-scale metabolic models for understanding microbial physiology. FEBS Lett 584: 2556–2564. - PubMed
-
- Price ND, Papin JA, Schilling CH, Palsson BO (2003) Genome-scale microbial in silico models: the constraints-based approach. Trends Biotechnol 21: 162–169. - PubMed
-
- Schuster S, Dandekar T, Fell DA (1999) Detection of elementary flux modes in biochemical networks: a promising tool for pathway analysis and metabolic engineering. Trends Biotechnol 17: 53–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

