Automated universal BRAF state detection within the activation segment in skin metastases by pyrosequencing-based assay U-BRAF(V600)
- PMID: 23555633
- PMCID: PMC3608589
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059221
Automated universal BRAF state detection within the activation segment in skin metastases by pyrosequencing-based assay U-BRAF(V600)
Abstract
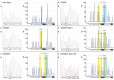
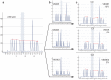
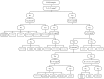
Malignant melanoma is a highly-aggressive type of malignancy with considerable metastatic potential and frequent resistance to cytotoxic agents. BRAF mutant protein was recently recognized as therapeutic target in metastatic melanoma. We present a newly-developed U-BRAF(V600) approach - a universal pyrosequencing-based assay for mutation detection within activation segment in exon 15 of human braf. We identified 5 different BRAF mutations in a single assay analyzing 75 different formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples of cutaneous melanoma metastases from 29 patients. We found BRAF mutations in 21 of 29 metastases. All mutant variants were quantitatively detectable by the newly-developed U-BRAF(V600) assay. These results were confirmed by ultra-deep-sequencing validation ((~)60,000-fold coverage). In contrast to all other BRAF state detection methods, the U-BRAF(V600) assay is capable of automated quantitative identification of at least 36 previously-published BRAF mutations. Under the precaution of a minimum of 3% mutated cells in front of a background of wild type cells, U-BRAFV600 assay design completely excludes false wild-type results. The corresponding algorithm for classification of BRAF-mutated variants is provided. The single-reaction assay and data analysis automation makes our approach suitable for the assessment of large clinical sample sizes. Therefore, we suggest U-BRAF(V600) assay as a most powerful sequencing-based diagnostic tool to automatically identify BRAF state as a prerequisite to targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lee JH, Choi JW, Kim YS (2011) Frequencies of BRAF and NRAS mutations are different in histological types and sites of origin of cutaneous melanoma: a meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol 164: 776–784. - PubMed
-
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr (2006) Melanoma. N Engl J Med 355: 51–65. - PubMed
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, et al. (2002) Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417: 949–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

