Picomonas judraskeda gen. et sp. nov.: the first identified member of the Picozoa phylum nov., a widespread group of picoeukaryotes, formerly known as 'picobiliphytes'
- PMID: 23555709
- PMCID: PMC3608682
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059565
Picomonas judraskeda gen. et sp. nov.: the first identified member of the Picozoa phylum nov., a widespread group of picoeukaryotes, formerly known as 'picobiliphytes'
Abstract
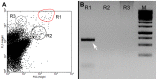
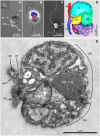
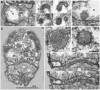
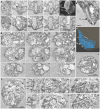
In 2007, a novel, putatively photosynthetic picoeukaryotic lineage, the 'picobiliphytes', with no known close eukaryotic relatives, was reported from 18S environmental clone library sequences and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Although single cell genomics later showed these organisms to be heterotrophic rather than photosynthetic, until now this apparently widespread group of pico-(or nano-)eukaryotes has remained uncultured and the organisms could not be formally recognized. Here, we describe Picomonas judraskeda gen. et sp. nov., from marine coastal surface waters, which has a 'picobiliphyte' 18S rDNA signature. Using vital mitochondrial staining and cell sorting by flow cytometry, a single cell-derived culture was established. The cells are biflagellate, 2.5-3.8×2-2.5 µm in size, lack plastids and display a novel stereotypic cycle of cell motility (described as the "jump, drag, and skedaddle"-cycle). They consist of two hemispherical parts separated by a deep cleft, an anterior part that contains all major cell organelles including the flagellar apparatus, and a posterior part housing vacuoles/vesicles and the feeding apparatus, both parts separated by a large vacuolar cisterna. From serial section analyses of cells, fixed at putative stages of the feeding cycle, it is concluded that cells are not bacterivorous, but feed on small marine colloids of less than 150 nm diameter by fluid-phase, bulk flow endocytosis. Based on the novel features of cell motility, ultrastructure and feeding, and their isolated phylogenetic position, we establish a new phylum, Picozoa, for Picomonas judraskeda, representing an apparently widespread and ecologically important group of heterotrophic picoeukaryotes, formerly known as 'picobiliphytes'.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
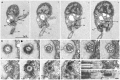

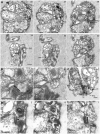

References
-
- Azam F, Fenchel T, Field JG, Gray JS, Meyer-Reil LA, et al. (1983) The ecological role of water column microbes in the sea. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 10: 257–263.
-
- Giovannoni SJ, Stingl U (2005) Molecular diversity and ecology of microbial plankton. Nature 437: 343–348. - PubMed
-
- Giovannoni SJ, Vergin KL (2012) Seasonality in ocean microbial communities. Science 335: 671–676. - PubMed
-
- Strom SL (2008) Microbial ecology of ocean biogeochemistry: a community perspective. Science 320: 1043–1045. - PubMed
-
- Sieburth JM, Smetacek V, Lenz J (1978) Pelagic ecosystem structure: heterotrophic compartments of the plankton and their relationship to plankton size fractions. Limnol Oceanogr 23: 1256–1263.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

