Role of a novel functional variant in the PPP2R1A promoter on the regulation of PP2A-Aalpha and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23555712
- PMCID: PMC3612049
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059574
Role of a novel functional variant in the PPP2R1A promoter on the regulation of PP2A-Aalpha and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
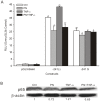
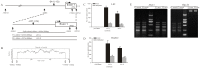
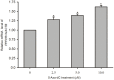
Previously, we identified the genetic variant -241 (-/G) (rs11453459) in the PP2A-Aα gene (PPP2R1A) promoter and demonstrated that this variant influences the DNA-binding affinity of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). In this study, we further confirmed that the transcriptional activity of PPP2R1A may be regulated by NF-κB through the functional genetic variant -241 (-/G). Moreover, we also demonstrated that the methylation status of CpG islands in the promoter of PPP2R1A influences the activity of this gene promoter. Few studies have examined the role of this -241 (-/G) variant in genetic or epigenetic regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To investigate whether this functional variant in the PPP2R1A promoter is associated with the risk of HCC and confirm the function of the -241 (-/G) variant in the HCC population, we conducted a case-control study involving 251 HCC cases and 252 cancer-free controls from a Han population in southern China. Compared with the -241 (--) homozygote, the heterozygous -241 (-G) genotype (adjusted OR = 0.32, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.17-0.58, P<0.001) and the -241 (-G)/(GG) genotypes (adjusted OR = 0.38, 95% CI = 0.22-0.67, P = 0.001) were both significantly associated with a reduced risk of HCC. Stratification analysis indicated that the protective role of -241 (-G) was more pronounced in individuals who were ≤ 40 years of age, female and HBV-negative. Our data suggest that the transcriptional activity of PPP2R1A is regulated by NF-κB through the -241 (-/G) variant and by the methylation of the promoter region. Moreover, the functional -241 (-/G) variant in the PPP2R1A promoter contributes to the decreased risk of HCC. These findings contribute novel information regarding the gene transcription of PPP2R1A regulated by the polymorphism and methylation in the promoter region through genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and functional analyses of polymorphism haplotypes of protein phosphatase 2A-Aα gene promoter.Mutat Res. 2011 Nov 1;716(1-2):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.08.004. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Mutat Res. 2011. PMID: 21889517
-
Effect of functional nuclear factor-kappaB genetic polymorphisms on hepatitis B virus persistence and their interactions with viral mutations on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Oncol. 2014 Dec;25(12):2413-2419. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu451. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25223483
-
TNF-α/NF-κB signaling epigenetically represses PSD4 transcription to promote alcohol-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Cancer Med. 2021 May;10(10):3346-3357. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3832. Epub 2021 May 1. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33932127 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of aberrant Wnt signaling in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6317-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6317. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical implications of DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma.HPB (Oxford). 2011 Jun;13(6):369-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2011.00303.x. Epub 2011 Mar 29. HPB (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21609368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variant of PP2A Subunit Gene Confers an Increased Risk of Primary Liver Cancer in Chinese.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Dec 1;14:1565-1574. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S335555. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34898995 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functions of transforming growth factor-β signaling in c-MYC driven hepatocellular carcinoma initiation and progression.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 19;12(2):200. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03488-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33608500 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between PP2A and microRNAs in Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2015 Feb 20;5:43. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00043. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25750899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex and Race-Related DNA Methylation Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 7;22(8):3820. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083820. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The broken "Off" switch in cancer signaling: PP2A as a regulator of tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and immune surveillance.BBA Clin. 2016 Aug 3;6:87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.08.002. eCollection 2016 Dec. BBA Clin. 2016. PMID: 27556014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moorhead GB, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Ulke-Lemee A (2007) Emerging roles of nuclear protein phosphatases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 234–244. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Possemato R, Campbell KT, Plattner CA, Pallas DC, et al. (2004) Identification of specific PP2A complexes involved in human cell transformation. Cancer Cell 5: 127–136. - PubMed
-
- Hemmings BA, Adams-Pearson C, Maurer F, Muller P, Goris J, et al. (1990) alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry 29: 3166–3173. - PubMed
-
- Hendrix P, Mayer-Jackel RE, Cron P, Goris J, Hofsteenge J, et al. (1993) Structure and expression of a 72-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Evidence for different size forms produced by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem 268: 15267–15276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

