Berberine ameliorates chronic kidney injury caused by atherosclerotic renovascular disease through the suppression of NFκB signaling pathway in rats
- PMID: 23555784
- PMCID: PMC3608549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059794
Berberine ameliorates chronic kidney injury caused by atherosclerotic renovascular disease through the suppression of NFκB signaling pathway in rats
Abstract
Background and objectives: Impaired renal function in atherosclerotic renovascular disease (ARD) may be the result of crosstalk between atherosclerotic renovascular stenosis and amplified oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis. Berberine (BBR) regulates cholesterol metabolism and exerts antioxidant effects. Accordingly, we hypothesized that BBR treatment may ameliorate ARD-induced kidney injury through its cholesterol-lowering effect and also suppression of the pathways involved in oxidative stress, inflammation and NFκB activation.
Methods: Male rats were subjected to unilateral renal artery stenosis with silver-irritant coil, and then fed with 12-week hypercholesterolemic diet. Rats with renal artery stenosis were randomly assigned to two groups (n = 6 each) - ARD, or ARD+BBR - according to diet alone or in combination with BBR. Similarly, age-matched rats underwent sham operation and were also fed with hypercholesterolemic diet alone or in combination with BBR as two corresponding controls. Single-kidney hemodynamic metrics were measured in vivo with Doppler ultrasound to determine renal artery flow. The metrics reflecting hyperlipidemia, oxidative stress, renal structure and function, inflammation and NFκB activation were measured, respectively.
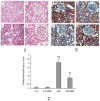
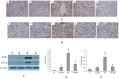
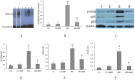
Results: Compared with control rats, ARD rats had a significant increase in urinary albumin, plasma cholesterol, LDL and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and a significant decrease in SOD activity. When exposed to 12-week BBR, ARD rats had significantly lower levels in blood pressure, LDL, urinary albumin, and TBARS. In addition, there were significantly lower expression levels of iNOS and TGF-β in the ARD+BBR group than in the ARD group, with attenuated NFκB-DNA binding activity and down-regulated protein levels of subunits p65 and p50 as well as IKKβ.
Conclusions: We conclude that BBR can improve hypercholesterolemia and redox status in the kidney, eventually ameliorating chronic renal injury in rats with ARD, and that BBR can act against proinflammatory and profibrotic responses through suppression of the NFκB signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Berberine ameliorates experimental diabetes-induced renal inflammation and fibronectin by inhibiting the activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Dec 5;381(1-2):56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.07.019. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23896433
-
Effect of Berberine on Activation of TLR4-NFκB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Patients with Gout.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):10-18. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3720-7. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36125615
-
Berberine in combination with evodiamine ameliorates gastroesophageal reflux disease through TAS2R38/TRPV1-mediated regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways and macrophage polarization.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156251. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156251. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39566409
-
Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Dec;243(2):449-61. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.09.032. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 26520899 Review.
-
Mechanisms of tissue injury in renal artery stenosis: ischemia and beyond.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Nov-Dec;52(3):196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2009.09.002. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009. PMID: 19917330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine alleviates chlorpyrifos-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 axis.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 29;10(3):e25233. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25233. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38327393 Free PMC article.
-
Sildenafil ameliorates oxidative stress and DNA damage in the stenotic kidneys in mice with renovascular hypertension.J Transl Med. 2014 Feb 6;12:35. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-35. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24502628 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 28;14:1217165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217165. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37701897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of berberine in Alzheimer's disease.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 Oct 3;12:2509-2520. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S114846. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27757035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cancer Prevention, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidation of Bioactive Phytochemicals Targeting the TLR4 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 12;19(9):2729. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092729. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30213077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF (2007) Chronic kidney disease: effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation 116: 85–97. - PubMed
-
- Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ, et al. (2006) Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes 55: 2256–2264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

