C. elegans ring finger protein RNF-113 is involved in interstrand DNA crosslink repair and interacts with a RAD51C homolog
- PMID: 23555887
- PMCID: PMC3610817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060071
C. elegans ring finger protein RNF-113 is involved in interstrand DNA crosslink repair and interacts with a RAD51C homolog
Abstract
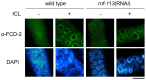
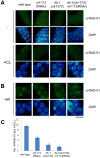
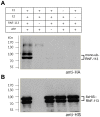
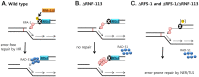
The Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway recognizes interstrand DNA crosslinks (ICLs) and contributes to their conversion into double-strand DNA breaks, which can be repaired by homologous recombination. Seven orthologs of the 15 proteins associated with Fanconi anemia are functionally conserved in the model organism C. elegans. Here we report that RNF-113, a ubiquitin ligase, is required for RAD-51 focus formation after inducing ICLs in C. elegans. However, the formation of foci of RPA-1 or FCD-2/FANCD2 in the FA pathway was not affected by depletion of RNF-113. Nevertheless, the RPA-1 foci formed did not disappear with time in the depleted worms, implying serious defects in ICL repair. As a result, RNF-113 depletion increased embryonic lethality after ICL treatment in wild-type worms, but it did not increase the ICL-induced lethality of rfs-1/rad51C mutants. In addition, the persistence of RPA-1 foci was suppressed in doubly-deficient rnf-113;rfs-1 worms, suggesting that there is an epistatic interaction between the two genes. These results lead us to suggest that RNF-113 and RFS-1 interact to promote the displacement of RPA-1 by RAD-51 on single-stranded DNA derived from ICLs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A PHF8 homolog in C. elegans promotes DNA repair via homologous recombination.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 8;10(4):e0123865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123865. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25853498 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans FANCD2 responds to replication stress and functions in interstrand cross-link repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Nov 8;5(11):1398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.06.010. Epub 2006 Aug 17. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16914393
-
DOG-1 is the Caenorhabditis elegans BRIP1/FANCJ homologue and functions in interstrand cross-link repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(5):1470-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01641-07. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18086896 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans: a model of Fanconi anemia and ICL repair.Mutat Res. 2009 Jul 31;668(1-2):103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.11.007. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 19059419 Review.
-
[The role of the Fanconi anemia pathway in DNA repair and maintenance of genome stability].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 May 8;68:459-72. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1101567. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 24864098 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Shear force-based genetic screen reveals negative regulators of cell adhesion and protrusive activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 12;114(37):E7727-E7736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616600114. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28847951 Free PMC article.
-
LIN-23, an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Component, Is Required for the Repression of CDC-25.2 Activity during Intestinal Development in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cells. 2016 Nov 30;39(11):834-840. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0238. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 27871172 Free PMC article.
-
The functional role of RNF113A in cervical carcinogenesis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Sep 1;12(9):3570-3582. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31934207 Free PMC article.
-
The X-linked trichothiodystrophy-causing gene RNF113A links the spliceosome to cell survival upon DNA damage.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 9;11(1):1270. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15003-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32152280 Free PMC article.
-
A novel truncating variant in ring finger protein 113A (RNF113A) confirms the association of this gene with X-linked trichothiodystrophy.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Mar;182(3):513-520. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61450. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 31880405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crossan GP, Patel KJ (2012) The Fanconi anaemia pathway orchestrates incisions at sites of crosslinked DNA. Journal of Pathology 226: 326–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

