Maternal complications and women's behavior in seeking care from skilled providers in North Gondar, Ethiopia
- PMID: 23555915
- PMCID: PMC3610646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060171
Maternal complications and women's behavior in seeking care from skilled providers in North Gondar, Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Maternal complications are morbidities suffered during pregnancy through the postpartum period of 42 days. In Ethiopia, little is known about women's experience of complications and their care-seeking behavior. This study attempted to assess experiences related to obstetric complication and seeking assistance from a skilled provider among women who gave birth in the last 12 months preceding the study.
Methods: This study was a cross-sectional survey of women who gave birth within one year preceding the study regardless of their delivery place. The study was carried out in six selected districts in North Gondar Zone, Amhara Region. Data was collected house-to-house in 12 selected clusters (kebeles) using a pretested Amharic questionnaire. During the survey, 1,668 women were interviewed. Data entry was done using Epi Info version 3.5.3 and was exported to SPSS for analysis. Logistic regression was applied to control confounders.
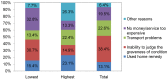
Results: Out of the total sample, 476 women (28.5%, 95% CI: 26.4%, 30.7%) reported some kind of complication. The most common complications reported were; excessive bleeding and prolonged labor that occurred mostly at the time of delivery and postpartum period. Out of the total women who faced complications, 248 (52.1%, 95% CI: 47.6%, 56.6%) sought assistance from a skilled provider. Inability to judge the severity of morbidities, distance/transport problems, lack of money/cost considerations and use of traditional options at home were the major reasons for not seeking care from skilled providers. Belonging to a wealthier quintile, getting antenatal care from a skilled provider and agreement of a woman in planning for possible complications were significantly associated with seeking assistance from a skilled provider.
Conclusion: Nearly half of the women who faced complications did not use skilled providers at the time of obstetric complications. Cognitive, geographic, economic and cultural barriers were involved in not using skilled maternal care.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ronsmans C, Graham WJ (2006) Maternal mortality: who, when, where, and why. Lancet 368: 1189–1200. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2010) Trends in maternal mortality: 1990 to 2008. Estimates developed by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA and The World Bank. Geneva: WHO.
-
- UN (2011) The Millennium Development Goals Report 28 –35.
-
- Bryce J, Daelmans B, Dwivedi A, Fauveau V, Lawn JE, et al. (2008) Countdown to 2015 for maternal, newborn, and child survival: the 2008 report on tracking coverage of interventions. Lancet 371: 1247–1258. - PubMed
-
- CSAEthiopia ICFinternational (2012) Ethiopia demographic and health survey 2011. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Calverton, Maryland, USA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical