Protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1δ (PPM1D) mRNA expression is a prognosis marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23556002
- PMCID: PMC3610683
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060775
Protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1δ (PPM1D) mRNA expression is a prognosis marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1δ (PPM1D) is an oncogene, overexpressed in many solid tumors, including ovarian cancer and breast cancer. The current study examined the expression and the prognostic value of PPM1D mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
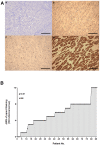
Methods: Total RNA was extracted from 86 HCC and paired non-cancerous liver tissues. PPM1D mRNA expression was determined by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Immunohistochemistry assay was used to verify the expression of ppm1d protein in the HCC and non-cancerous liver tissues. HCC patients were grouped according to PPM1D mRNA expression with the average PPM1D mRNA level in non-cancerous liver tissue samples as the cut-off. Correlations between clinicopathologic variables, overall survival and PPM1D mRNA expression were analyzed.
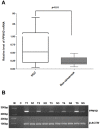
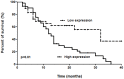
Findings: PPM1D mRNA was significantly higher in HCC than in the paired non-cancerous tissue (p<0.01). This was confirmed by ppm1d staining. 56 patients were classified as high expression group and the other 30 patients were categorized as low expression group. There were significant differences between the two groups in term of alpha-fetoprotein (α-FP) level (p<0.01), tumor size (p<0.01), TNM stage (p<0.01), recurrence incidence (p<0.01) and family history of liver cancer (p<0.01). The current study failed to find significant differences between the two groups in the following clinical characteristics: age, gender, portal vein invasion, lymphnode metastasis, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and alcohol intake. Survival time of high expression group was significantly shorter than that of low expression group (median survival, 13 months and 32 months, respectively, p<0.01).
Conclusion: Up-regulation of PPM1D mRNA was associated with progressive pathological feature and poor prognosis in HCC patients. PPM1D mRNA may serve as a prognostic marker in HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hussain SP, Schwank J, Staib F, Wang XW, Harris CC (2007) TP53 mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma: insights into the etiology and pathogenesis of liver cancer. Oncogene 26: 2166–2176. - PubMed
-
- Staib F, Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Wang XW, Harris CC (2003) TP53 and liver carcinogenesis. Hum Mutat 21: 201–216. - PubMed
-
- Mazzanti R, Gramantieri L, Bolondi L (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and clinical aspects. Mol Aspects Med 29: 130–143. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

