Nightmares that mislead to diagnosis of reactivation of PTSD
- PMID: 23556065
- PMCID: PMC3615167
- DOI: 10.3402/ejpt.v4i0.18714
Nightmares that mislead to diagnosis of reactivation of PTSD
Abstract
Background: Sleep disturbance is a common characteristic of patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Besides the clinical descriptions of nightmares and insomnia, periodic limb movements (PLMs) are reported to co-occur in PTSD. Although the causal relationship between sleep disturbance and PTSD is not fully understood, sleep disturbance is an independent risk factor for the development and reactivation of PTSD. In contrast, the link between PTSD and REM sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) is less clear.
Method: A case report is presented to illustrate differential diagnosis and time course of sleep disturbance in the context of PTSD.
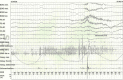
Result: A 63-year-old man who had been successfully treated for PTSD but who suffered the re-occurrence of disturbed sleep due to RBD and PLM, which was misdiagnosed as reactivation of PTSD.
Conclusions: RBD can mimic PTSD-related nightmares. Accurate diagnosis of sleep disturbance in PTSD is relevant for treatment and prognostic evaluation.
Keywords: REM sleep behaviour disorder; nightmares; periodic limb movements; posttraumatic stress disorder; sleep disturbance.
Figures
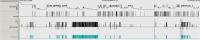
References
-
- Al-Saffar S, Borgå P, Hällström T. Long-term consequences of unrecognised PTSD in general outpatient psychiatry. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 2002;37:580–585. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Archibald H. C, Tuddenham R. D. Persistent stress reaction after combat: A 20-year follow-up. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1965;12:475–481. - PubMed
-
- Belleville G, Guay S, Marchand A. Persistence of sleep disturbances following cognitive-behavior therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2011;70:318–327. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
