Robust detection of dynamic community structure in networks
- PMID: 23556979
- PMCID: PMC3618100
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4790830
Robust detection of dynamic community structure in networks
Abstract
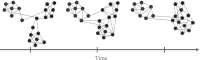
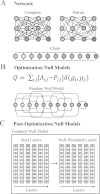
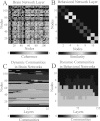
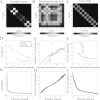
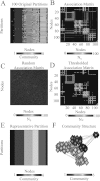
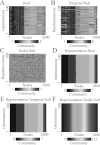
We describe techniques for the robust detection of community structure in some classes of time-dependent networks. Specifically, we consider the use of statistical null models for facilitating the principled identification of structural modules in semi-decomposable systems. Null models play an important role both in the optimization of quality functions such as modularity and in the subsequent assessment of the statistical validity of identified community structure. We examine the sensitivity of such methods to model parameters and show how comparisons to null models can help identify system scales. By considering a large number of optimizations, we quantify the variance of network diagnostics over optimizations ("optimization variance") and over randomizations of network structure ("randomization variance"). Because the modularity quality function typically has a large number of nearly degenerate local optima for networks constructed using real data, we develop a method to construct representative partitions that uses a null model to correct for statistical noise in sets of partitions. To illustrate our results, we employ ensembles of time-dependent networks extracted from both nonlinear oscillators and empirical neuroscience data.
Figures
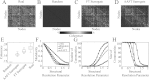

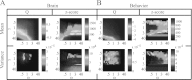
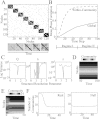
References
-
- Newman M. E. J., Networks: An Introduction (Oxford University Press, 2010).
-
- Holme P. and Saramäki J., Phys. Rep. 519, 97 (2012). 10.1016/j.physrep.2012.03.001 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

