Generation and in vivo characterization of a chimeric αvβ5-targeting antibody 14C5 and its derivatives
- PMID: 23557246
- PMCID: PMC3626673
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-219X-3-25
Generation and in vivo characterization of a chimeric αvβ5-targeting antibody 14C5 and its derivatives
Abstract
Background: Previous studies showed that radiolabeled murine monoclonal antibody (mAb) 14C5 and its Fab and F(ab')2 fragments, targeting αvβ5 integrin, have promising properties for diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. To diminish the risk of generating a human anti-mouse antibody response in patients, chimeric variants were created. The purpose of this study was to recombinantly produce chimeric antibody (chAb) derivatives of the murine mAb 14C5 and to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo characteristics.
Methods: In vitro stability, specificity, and affinity of radioiodinated chAb and fragments (Iodo-Gen method) were examined on high-expressing αvβ5 A549 lung tumor cells. In vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetic characteristics were studied in A549 lung tumor-bearing Swiss Nu/Nu mice.
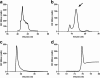
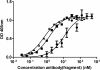
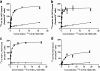
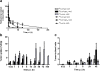
Results: Saturation binding experiments revealed high in vitro affinity of radioiodinated chAb, F(ab')2, and Fab, with dissociation constants (KD) of 1.19 ± 0.19, 0.68 ± 0.10, and 2.11 ± 0.58 nM, respectively. ChAb 14C5 showed highest tumor uptake (approximately 10%ID/g) at 24 h post injection, corresponding with other high-affinity Abs. ChF(ab')2 and chFab fragments showed faster clearance from the blood compared to the intact Ab.
Conclusions: The chimerization of mAb 14C5 and its fragments has no or negligible effect on the properties of the antibody. In vitro and in vivo properties show that the chAb 14C5 is promising for radioimmunotherapy, due to its high maximum tumor uptake and its long retention in the tumor. The chF(ab')2 fragment shows a similar receptor affinity and a faster blood clearance, causing less non-specific retention than the chAb. Due to their fast blood clearance, the fragments show high potential for radioimmunodiagnosis.
Figures
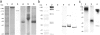

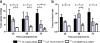
Similar articles
-
Biodistribution and planar gamma camera imaging of (123)I- and (131)I-labeled F(ab')(2) and Fab fragments of monoclonal antibody 14C5 in nude mice bearing an A549 lung tumor.Nucl Med Biol. 2007 Apr;34(3):257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2006.12.006. Nucl Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17383575
-
123/131I-Fab and F(ab')2 fragments of anti-integrin αvβ5 monoclonal antibody 14C5.2013 Mar 20 [updated 2013 May 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2013 Mar 20 [updated 2013 May 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23700642 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Optimization of IGF-1R SPECT/CT imaging using 111In-labeled F(ab')2 and Fab fragments of the monoclonal antibody R1507.Mol Pharm. 2012 Aug 6;9(8):2314-21. doi: 10.1021/mp300232n. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22747077
-
Radiolabeling, biodistribution, and dosimetry of (123)I-mAb 14C5: a new mAb for radioimmunodetection of tumor growth and metastasis in vivo.J Nucl Med. 2004 Jun;45(6):1065-73. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15181142
-
Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of genetically-engineered antibodies.Q J Nucl Med. 1998 Dec;42(4):225-41. Q J Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9973838 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of a F(ab')2 Fragment as the Targeting Agent of α-Radiation Therapy: A Comparison of the Therapeutic Benefit of Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Administered Radioimmunotherapy.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2018 Jun;33(5):182-193. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2018.2434. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2018. PMID: 29916748 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

