Bacterial expression strategies for several Sus scrofa diacylglycerol kinase alpha constructs: solubility challenges
- PMID: 23558375
- PMCID: PMC3617429
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01609
Bacterial expression strategies for several Sus scrofa diacylglycerol kinase alpha constructs: solubility challenges
Abstract
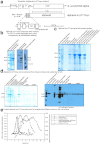
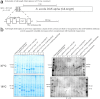
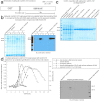
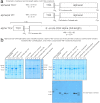
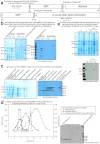
We pursued several strategies for expressing either full-length Sus scrofa diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) alpha or the catalytic domain (alphacat) in Escherichia coli. Alphacat could be extracted, refolded, and purified from inclusion bodies, but when subjected to analytical gel filtration chromatography, it elutes in the void volume, in what we conclude are microscopic aggregates unsuitable for x-ray crystallography. Adding glutathione S-transferase, thioredoxin, or maltose binding protein as N-terminal fusion tags did not improve alphacat's solubility. Coexpressing with bacterial chaperones increased the yield of alphacat in the supernatant after high-speed centrifugation, but the protein still elutes in the void upon analytical gel filtration chromatography. We believe our work will be of interest to those interested in the structure of eukaryotic DGKs, so that they know which expression strategies have already been tried, as well as to those interested in protein folding and those interested in chaperone/target-protein interactions.
Figures

References
-
- Takeishi Y., Goto K. & Kubota I. Role of diacylglycerol kinase in cellular regulatory processes: a new regulator for cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Pharmacol. Ther. 115, 352–359 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ali H. et al. Selective translocation of diacylglycerol kinase zeta in hippocampal neurons under transient forebrain ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 372, 190–195 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Kanoh H. & Ohno K. Partial purification and properties of diacylglycerol kinase from rat liver cytosol. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 209, 266–275 (1981). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

