Prenatal and postnatal inflammation in relation to cortisol levels in preterm infants at 18 months corrected age
- PMID: 23558431
- PMCID: PMC3819325
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2013.24
Prenatal and postnatal inflammation in relation to cortisol levels in preterm infants at 18 months corrected age
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether early inflammation is related to cortisol levels at 18 months corrected age (CA) in children born very preterm.
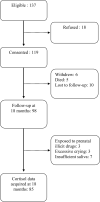
Study design: Infants born ≤ 32 weeks of gestational age were recruited in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and placental histopathology, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and chart review were obtained. At 18 months CA, developmental assessment and collection of three salivary cortisol samples were carried out. Generalized least squares was used to analyze data from 85 infants providing 222 cortisol samples.
Result: Infants exposed to chorioamnionitis with funisitis had a significantly different pattern of cortisol across the samples compared with infants with chorioamnionitis alone or no prenatal inflammation (F(4, 139)=7.3996, P<0.0001). Postnatal infections, necrotizing enterocolitis and chronic lung disease were not significantly associated with the cortisol pattern at 18 months CA.
Conclusion: In children born very preterm, prenatal inflammatory stress may contribute to altered programming of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Birth weight and postnatal growth in preterm born children are associated with cortisol in early infancy, but not at age 8 years.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017 Aug;82:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 4. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28511047
-
Association of plasma cortisol and chronic lung disease in preterm infants.Pediatrics. 2001 Mar;107(3):494-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.3.494. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11230588 Clinical Trial.
-
Pain-related stress in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and salivary cortisol reactivity to socio-emotional stress in 3-month-old very preterm infants.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016 Oct;72:161-5. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Jul 10. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27428089
-
Development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in the fetus and preterm infant.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jun;15(6):759-69. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2002.15.6.759. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12099385 Review.
-
The Val66Met brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene variant interacts with early pain exposure to predict cortisol dysregulation in 7-year-old children born very preterm: Implications for cognition.Neuroscience. 2017 Feb 7;342:188-199. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.044. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 26318333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saliva cortisol diurnal variation and stress responses in term and preterm infants.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022 Sep;107(5):558-564. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-321593. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022. PMID: 35256524 Free PMC article.
-
Preterm birth: A neuroinflammatory origin for metabolic diseases?Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Mar 7;37:100745. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100745. eCollection 2024 May. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 38511150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local injury and systemic infection in infants alter later nociception and pain affect during early life and adulthood.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Nov 10;9:100175. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100175. eCollection 2020 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 34589906 Free PMC article.
-
Annual Research Review: Early adversity, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis, and child psychopathology.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;59(4):327-346. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12784. Epub 2017 Jul 17. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28714126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 in pregnancy: Placental and neonatal involvement.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2020 Nov;84(5):e13306. doi: 10.1111/aji.13306. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32779810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hillier SL, Martius J, Krohn M, Kiviat N, Holmes KK, Eschenbach DA. A case-control study of chorioamnionic infection and histologic chorioamnionitis in prematurity. N Engl J Med. 1988;13319(15):972–978. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N. Infections in VLBW infants: studies from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Semin Perinatol. 2003;27(4):293–301. - PubMed
-
- Wirbelauer J, Seidenspinner S, Thomas W, Kunzmann S, Speer CP. Funisitis is associated with increased interleukin-10 gene expression in cord blood mononuclear cells in preterm infants </=32 weeks of gestation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011;155(1):31–35. - PubMed
-
- Harris MC, D'Angio CT, Gallagher PR, Kaufman D, Evans J, Kilpatrick L. Cytokine elaboration in critically ill infants with bacterial sepsis, necrotizing entercolitis, or sepsis syndrome: correlation with clinical parameters of inflammation and mortality. J Pediatr. 2005;147(4):462–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

