Cloning of a hamster anti-mouse CD79B antibody sequences and identification of a new hamster immunoglobulin lambda constant IGLC gene region
- PMID: 23558558
- PMCID: PMC3686505
- DOI: 10.1007/s00251-013-0698-5
Cloning of a hamster anti-mouse CD79B antibody sequences and identification of a new hamster immunoglobulin lambda constant IGLC gene region
Abstract
Anti-CD79 antibodies have been effective at targeting B cell lymphoma cells and depleting B cells in animal models. In order to engineer recombinant antibodies with additional effector functions in mice, we cloned and sequenced the full-length cDNAs of the heavy and light chain of a hamster anti-mouse CD79B antibody. Although hamster antibodies represent a unique source of monoclonal antibodies against mouse, rat, and human antigens, sequence information of hamster immunoglobulins (IG) is sparse. Here, we report a new hamster (Cricetulus migratorius) IG lambda constant (IGLC) gene region that is most homologous to mouse IGLC2 and IGLC3.
Figures
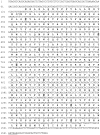
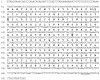

References
-
- Alegre ML, Tso JY, Sattar HA, Smith J, Desalle F, Cole M, Bluestone JA. An anti-murine CD3 monoclonal antibody with a low affinity for Fc gamma receptors suppresses transplantation responses while minimizing acute toxicity and immunogenicity. J Immunol. 1995;155:1544–1555. - PubMed
-
- Carter PJ. Potent antibody therapeutics by design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:343–357. - PubMed
-
- Collins M, Whitters MJ. Hamster cDNA homologs to the mouse immunoglobulin IgG2 constant and Igh-VH10 genes. Immunogenetics. 1995;42:225–226. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenmann FF, Lefranc MP. IMGT/DomainGapAlign: IMGT standardized analysis of amino acid sequences of variable, constant, and groove domains (IG, TR, MH, IgSF, MhSF) Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2011;2011:737–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

