Alternative pyrimidine biosynthesis protein ApbE is a flavin transferase catalyzing covalent attachment of FMN to a threonine residue in bacterial flavoproteins
- PMID: 23558683
- PMCID: PMC3656284
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455402
Alternative pyrimidine biosynthesis protein ApbE is a flavin transferase catalyzing covalent attachment of FMN to a threonine residue in bacterial flavoproteins
Abstract
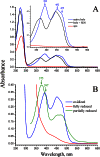
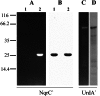
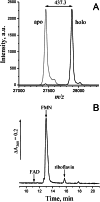
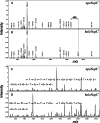
Na(+)-translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (Na(+)-NQR) contains two flavin residues as redox-active prosthetic groups attached by a phosphoester bond to threonine residues in subunits NqrB and NqrC. We demonstrate here that flavinylation of truncated Vibrio harveyi NqrC at Thr-229 in Escherichia coli cells requires the presence of a co-expressed Vibrio apbE gene. The apbE genes cluster with genes for Na(+)-NQR and other FMN-binding flavoproteins in bacterial genomes and encode proteins with previously unknown function. Experiments with isolated NqrC and ApbE proteins confirmed that ApbE is the only protein factor required for NqrC flavinylation and also indicated that the reaction is Mg(2+)-dependent and proceeds with FAD but not FMN. Inactivation of the apbE gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae, wherein the nqr operon and apbE are well separated in the chromosome, resulted in a complete loss of the quinone reductase activity of Na(+)-NQR, consistent with its dependence on covalently bound flavin. Our data thus identify ApbE as a novel modifying enzyme, flavin transferase.
Keywords: Bacterial Metabolism; FMN; Flavoproteins; Na+-translocating NADH:Quinone Oxidoreductase; Post-translational Modification; Respiratory Chain.
Figures





References
-
- Verkhovsky M. I., Bogachev A. V. (2010) Sodium-translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase as a redox-driven ion pump. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1797, 738–746 - PubMed
-
- Zhou W., Bertsova Y. V., Feng B., Tsatsos P., Verkhovskaya M. L., Gennis R. B., Bogachev A. V., Barquera B. (1999) Sequencing and preliminary characterization of the Na+-translocating NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase from Vibrio harveyi. Biochemistry 38, 16246–16252 - PubMed
-
- Nakayama Y., Hayashi M., Unemoto T. (1998) Identification of six subunits constituting Na+-translocating NADH-quinone reductase from the marine Vibrio alginolyticus. FEBS Lett. 422, 240–242 - PubMed
-
- Rich P. R., Meunier B., Ward F. B. (1995) Predicted structure and possible ion-motive mechanism of the sodium-linked NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase of Vibrio alginolyticus. FEBS Lett. 375, 5–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

