Corpus callosum integrity and neuropsychological performance after traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study
- PMID: 23558829
- PMCID: PMC4918513
- DOI: 10.1097/HTR.0b013e318289ede5
Corpus callosum integrity and neuropsychological performance after traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study
Abstract
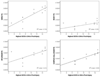
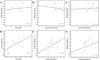
Objectives: (1) Detailed analysis of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters (fractional anisotropy and radial diffusivity) to evaluate white matter integrity in the corpus callosum (CC), and (2) examine correlations between DTI data and performance on multiple measures of cognitive functioning.
Participants: Twelve individuals with a history of complicated mild, moderate, or severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) who were an average of 1.7 years postinjury and 12 control participants.
Main measures: Standardized and experimental neuropsychological tests; detailed analysis of DTI parameters.
Results: The TBI group demonstrated DTI values suggesting decreased white matter integrity and correlations with severity of injury. Both groups showed correlations between DTI parameters and cognitive measures, with more significant correlations observed for the TBI group. White matter changes in the CC were evident chronically and were related to severity of injury.
Conclusions: Diffusion tensor imaging parameters suggesting disruptions in white matter in the CC may be implicated in impaired performance, both in terms of cognitive tasks and reaction time, after TBI.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Callosal Function in Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Linked to Disrupted White Matter Integrity.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;35(28):10202-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1595-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26180196 Free PMC article.
-
Whole brain and corpus callosum diffusion tensor metrics: How do they correlate with visual and verbal memory performance in chronic traumatic brain injury.J Integr Neurosci. 2019 Jun 30;18(2):95-105. doi: 10.31083/j.jin.2019.02.144. J Integr Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31321950
-
Longitudinal changes in the corpus callosum following pediatric traumatic brain injury.Dev Neurosci. 2010;32(5-6):361-73. doi: 10.1159/000317058. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20948181 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging of traumatic brain injury review: implications for neurorehabilitation.NeuroRehabilitation. 2012;31(3):281-93. doi: 10.3233/NRE-2012-0796. NeuroRehabilitation. 2012. PMID: 23093455 Review.
-
The relationship between diffusion tensor imaging findings and cognitive outcomes following adult traumatic brain injury: A meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Sep;92:93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.05.023. Epub 2018 May 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 29803527 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing Postconcussive Reaction Time Using Transport-Based Morphometry of Diffusion Tensor Images.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Jul;40(7):1117-1123. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6087. Epub 2019 Jun 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 31196860 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical lesions and focal white matter injury are associated with attentional performance in chronic traumatic brain injury.Brain Commun. 2024 Nov 21;7(1):fcae420. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae420. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 39926612 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting axonal injury in individual patients after traumatic brain injury.Brain. 2021 Feb 12;144(1):92-113. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa372. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33257929 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of the corpus callosum and inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus in recovery after traumatic brain injury.Neuroradiology. 2025 Jun;67(6):1495-1510. doi: 10.1007/s00234-025-03577-2. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 40067461
-
Neuroimaging Biomarkers of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy: Targets for the Academic Memory Disorders Clinic.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Apr;18(2):772-791. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01028-3. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33847906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG. Traumatic brain injury in the United States: Emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control; 2010.
-
- Ricker JH. Traumatic brain injury. In: Frank R, Rosenthal M, Caplan BT, editors. Handbook of Rehabilitation Psychology. 2nd. Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association Press; 2010. pp. 43–62.
-
- Meythaler JM, Peduzzi JD, Eleftheriou E, Novack TA. Current concepts: diffuse axonal injury—associated traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:1461–1471. - PubMed
-
- Büki A, Povlishock JT. All roads lead to disconnection?--Traumatic axonal injury revisited. Acta Neurochirurgica. 2006;148:181–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources