mRNA-binding protein ZFP36 is expressed in atherosclerotic lesions and reduces inflammation in aortic endothelial cells
- PMID: 23559629
- PMCID: PMC3844532
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301496
mRNA-binding protein ZFP36 is expressed in atherosclerotic lesions and reduces inflammation in aortic endothelial cells
Abstract
Objective: We studied the expression and function of an mRNA-binding protein, zinc finger protein-36 (ZFP36), in vascular endothelial cells in vivo and in vitro. We tested the hypotheses that ZFP36 regulates inflammation in vascular endothelial cells and that it functions through direct binding to target cytokine mRNAs. We also tested whether ZFP36 inhibits nuclear factor-κB-mediated transcriptional responses in vascular endothelial cells.
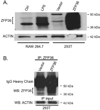
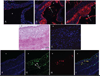
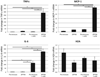
Approach and results: ZFP36 was minimally expressed in healthy aorta but was expressed in endothelial cells overlying atherosclerotic lesions in mice and humans. The protein was also expressed in macrophage foam cells of atherosclerosis. ZFP36 was expressed in human aortic endothelial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide, glucocorticoid, and forskolin, but not oxidized low-density lipoproteins or angiotensin II. Functional studies demonstrated that ZFP36 reduces the expression of inflammatory cytokines in target cells by 2 distinct mechanisms: ZFP36 inhibits nuclear factor-κB transcriptional activation and also binds to cytokine mRNAs, leading to reduced transcript stability.
Conclusions: ZFP36 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and macrophage foam cells where it inhibits the expression of proinflammatory mRNA transcripts. The anti-inflammatory effects of ZFP36 in endothelial cells occur via both transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Our data suggest that enhancing vascular ZFP36 expression might reduce vascular inflammation.
Keywords: AU-rich element; atherosclerosis; cytokines; endothelial cell; inflammation; zinc finger protein-36.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA129424/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL095070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12-HD000849/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01HL095070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091841/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1ZIAES090080-15/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 HL090584/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HD059909/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL070531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS055077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD059909/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK091841/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD000849/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD055379/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD055379/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA129424/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL090584/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

