MicroRNA-93 controls perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia by modulating expression of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway
- PMID: 23559675
- PMCID: PMC3856290
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000860
MicroRNA-93 controls perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia by modulating expression of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are key regulators of gene expression in response to injury, but there is limited knowledge of their role in ischemia-induced angiogenesis, such as in peripheral arterial disease. Here, we used an unbiased strategy and took advantage of different phenotypic outcomes that follow surgically induced hindlimb ischemia between inbred mouse strains to identify key microRNAs involved in perfusion recovery from hindlimb ischemia.
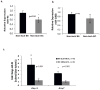
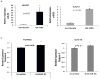
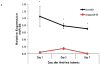
Methods and results: From comparative microRNA profiling between inbred mouse strains that display profound differences in their extent of perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia, we found that the mouse strain with higher levels of microRNA-93 (miR-93) in hindlimb muscle before ischemia and the greater ability to upregulate miR-93 in response to ischemia had better perfusion recovery. In vitro, overexpression of miR-93 attenuated hypoxia-induced apoptosis in both endothelial and skeletal muscle cells and enhanced proliferation in both cell types. In addition, miR-93 overexpression enhanced endothelial cell tube formation. In vivo, miR-93 overexpression enhanced capillary density and perfusion recovery from hindlimb ischemia, and antagomirs to miR-93 attenuated perfusion recovery. Both in vitro and in vivo modulation of miR-93 resulted in alterations in the expression of >1 cell cycle pathway gene in 2 different cell types.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that miR-93 enhances perfusion recovery from hindlimb ischemia by modulation of multiple genes that coordinate the functional pathways of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Thus, miR-93 is a strong potential target for pharmacological modulation to promote angiogenesis in ischemic tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









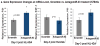
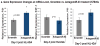
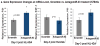
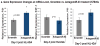
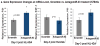
Similar articles
-
Loss of interleukin-21 receptor activation in hypoxic endothelial cells impairs perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 May;35(5):1218-25. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305476. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25838422 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-6236 Regulation of Postischemic Skeletal Muscle Angiogenesis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Dec 3;13(23):e035923. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.035923. Epub 2024 Nov 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39604034 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-133a impairs perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia in diabetic mice.Biosci Rep. 2018 Jul 2;38(4):BSR20180346. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180346. Print 2018 Aug 31. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29789398 Free PMC article.
-
HypoxamiR regulation and function in ischemic cardiovascular diseases.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Sep 10;21(8):1202-19. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5403. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24053126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: key modulators of posttranscriptional gene expression.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jan;136(1):17-25. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.11.028. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19049808 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular Disease and miRNAs: Possible Oxidative Stress-Regulating Roles of miRNAs.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 27;13(6):656. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060656. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA-93 in regulation of angiogenesis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):10609-13. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2605-6. Epub 2014 Sep 14. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25217985 Review.
-
Epigenetics and Peripheral Artery Disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016 Apr;18(4):15. doi: 10.1007/s11883-016-0567-4. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016. PMID: 26888065 Review.
-
A multiscale computational model predicts distribution of anti-angiogenic isoform VEGF165b in peripheral arterial disease in human and mouse.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 17;6:37030. doi: 10.1038/srep37030. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27853189 Free PMC article.
-
miR-25/93 mediates hypoxia-induced immunosuppression by repressing cGAS.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;19(10):1286-1296. doi: 10.1038/ncb3615. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28920955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Sun W, Julie Li YS, Huang HD, Shyy JY, Chien S. microRNA: a master regulator of cellular processes for bioengineering systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, Sandusky GE, Zhang Q, Zhao G. Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9330–9335. - PubMed
-
- Lee KH, Chen YL, Yeh SD, Hsiao M, Lin JT, Goan YG, Lu PJ. MicroRNA-330 acts as tumor suppressor and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through E2F1-mediated suppression of Akt phosphorylation. Oncogene. 2009;28:3360–3370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

