Effect of dry heat and steam sterilization on load-deflection characteristics of β-titanium wires: An in vitro study
- PMID: 23559917
- PMCID: PMC3612189
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-3327.104871
Effect of dry heat and steam sterilization on load-deflection characteristics of β-titanium wires: An in vitro study
Abstract
Background: Sterilization techniques could affect the characteristics of orthodontic wires. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of steam and dry heat sterilization techniques on load-deflection behavior of five types of β-titanium alloy wires.
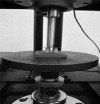
Materials and methods: The samples consisted of 30 straight lengths of five types of β-titanium alloy wires: Titanium Molybdenum Alloy (TMA) Low Friction (TMAL), TMA Low Friction Colored (HONE), Resolve (RES), BetaForce (BETA), and BETA CNA (CNA). Thirty wire segments were divided into three groups of 10. Group 1 was the control group and the group 2 samples were sterilized by dry heat in an oven (60 minutes at 160°C) and group 3 by steam in an autoclave (15 minutes at 121°C). Then all the wire samples underwent a three-point bending test in a testing machine to evaluate load-deflection properties. Data was analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA and Scheffé's test (α = 0.05).
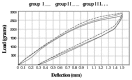
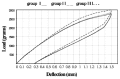
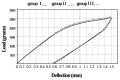
Results: The results showed that dry heat sterilization significantly increased force levels during both loading and unloading of CNA, BETA and RES and during loading of HONE (P < 0.05). Steam sterilization significantly increased force levels during both loading and unloading of BETA and during unloading of HONE (P < 0.05), with no effects on the load-deflection characteristics of TMAL, CNA and RES (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: It appears dry heat sterilization increases stiffness of RES, BETA, CNA and HONE but autoclave sterilization did not have any effect on load-deflection characteristics of most of the β-titanium wires tested, indicating that clinicians who want to provide maximum safety for their patients can autoclave TMAL, RES and CNA before applying them.
Keywords: Beta titanium; orthodontic wire; sterilization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Load-deflection characteristics of nickel-titanium alloy wires after clinical recycling and dry heat sterilization.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992 Aug;102(2):120-6. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(92)70023-4. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992. PMID: 1636628
-
Evaluating the effect of clinical usage and autoclave sterilization on the load deflection properties of three different orthodontic wires: Ex-vivo study.Int Orthod. 2019 Sep;17(3):469-477. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Int Orthod. 2019. PMID: 31383599
-
The effect of different clinical recycling methods on load deflection properties of super-elastic and thermal nickel-titanium orthodontic arch wires: A comparative assessment.J Orthod Sci. 2024 Sep 17;13:27. doi: 10.4103/jos.jos_200_23. eCollection 2024. J Orthod Sci. 2024. PMID: 39450219 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical properties of beta-titanium wires.Angle Orthod. 2011 May;81(3):478-83. doi: 10.2319/070510-379.1. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Angle Orthod. 2011. PMID: 21299389 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical properties and clinical applications of orthodontic wires.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989 Aug;96(2):100-9. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(89)90251-5. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989. PMID: 2667330 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of different sterilization methods on surface characteristics and biofilm formation on zirconia in vitro.Dent Mater. 2018 Feb;34(2):272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.11.012. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Dent Mater. 2018. PMID: 29183674 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of autoclave cycles on the mechanical properties and surface roughness of NiTi archwires: ex-vivo study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 24;24(1):1284. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04877-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39448972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cash RG. Trends in sterilization and disinfection procedures in orthodontic offices. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1990;98:292–9. - PubMed
-
- Payne GS. Sterilization and disinfection in the orthodontic Office: A practical approach. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1986;90:250–2. - PubMed
-
- Mulick JF. Upgrading sterilization in the orthodontic Practice. Am J Orthod. 1986;89:346–51. - PubMed
-
- Kangane SK, Sawant SK, Patil PS. Instrument Sterilization in the orthodontic clinic: A review. Int Journal of Clinical Dental Science. 2010;1:53–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
