Association between maternal education and diet of children at 9 months is partially explained by mothers' diet
- PMID: 23560743
- PMCID: PMC6860322
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12031
Association between maternal education and diet of children at 9 months is partially explained by mothers' diet
Abstract
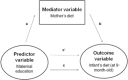
Infants of mothers of low educational background display consistently poorer outcomes, including suboptimal weaning diets. Less is known about the different causal pathways that relate maternal education to infants' diet. The present study aimed to test the hypothesis that the relationship between maternal education and infants' diet is mediated by mothers' diet. The analyses included 421 mother-infant pairs from the Melbourne Infant Feeding Activity and Nutrition Trial (InFANT) Program. Dietary intakes were collected from mothers when infants were aged 3 months, using a validated food frequency questionnaire relating to the past year, and in infants aged 9 months using 3 × 24-h recalls. Principal component analysis was used to derive dietary pattern scores, based on frequencies of 55 food groups in mothers, and intakes of 23 food groups in infants. Associations were assessed with multivariable linear regression. We tested the product 'ab' to address the mediation hypothesis, where 'a' refers to the relationship between the predictor variable (education) and the mediator variable (mothers' diet), and 'b' refers to the association between the mediator variable and the outcome variable (infants' diet), controlling for the predictor variable. Maternal scores on the 'Fruit and vegetables' dietary pattern partially mediated the relationships between maternal education and two infant dietary patterns, namely 'Balanced weaning diet' [ab = 0.11; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.04; 0.18] and 'Formula' (ab = -0.08; 95%CI: -0.15; -0.02). These findings suggest that targeting pregnant mothers of low education level with the aim of improving their own diet may also promote better weaning diets in their infants.
Keywords: dietary patterns; education; infants; mediation; mothers.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barker D.J., Osmond C., Forsen T.J., Kajantie E. & Eriksson J.G. (2005) Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. New England Journal of Medicine 353, 1802–1809. - PubMed
-
- Blanton C.A., Moshfegh A.J., Baer D.J. & Kretsch M.J. (2006) The USDA automated multiple‐pass method accurately estimates group total energy and nutrient intake. Journal of Nutrition 136, 2594–2599. - PubMed
-
- Braveman P.A., Cubbin C., Egerter S., Chideya S., Marchi K.S., Metzler M. et al (2005) Socioeconomic status in health research: one size does not fit all. Journal of the American Medical Association 294, 2879–2888. - PubMed
-
- Brekke H.K., Van Odijk J. & Ludvigsson J. (2007) Predictors and dietary consequences of frequent intake of high‐sugar, low‐nutrient foods in 1‐year‐old children participating in the ABIS study. British Journal of Nutrition 97, 176–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

