Clinical evaluation of a prototype multi-bending peroral direct cholangioscope
- PMID: 23560942
- PMCID: PMC3933760
- DOI: 10.1111/den.12082
Clinical evaluation of a prototype multi-bending peroral direct cholangioscope
Abstract
Background: Although peroral direct cholangioscopy (PDCS) is emerging as an alternative to traditional mother-daughter cholangioscopy, it is associated with high failure rates. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the ability to insert and carry out interventions using a prototype multi-bending PDCS.
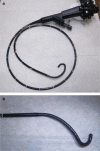
Patients and methods: Prospective, observational clinical feasibility study was done in 41 patients with a variety of biliary diseases. A multi-bending PDCS prototype was inserted using a free-hand technique, a guidewire alone, or with a 5-Fr diameter anchoring balloon. Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures were carried out.
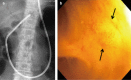
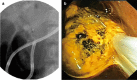
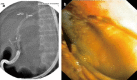
Results: The free-hand direct insertion technique failed in all attempted cases (n = 7). Of the remaining 34 cases, successful rate of PDCS insertion into the distal bile duct was achieved by passing the PDCS over a guidewire alone (n = 6) and/or with a guidewire plus anchoring balloon (n = 28) for an overall successrate of 88.2% (30/34). In 13 (92.9%) patients without an underlying biliary stricture, PDCS insertion proximal to the bifurcation was possible. In 25 cases, biliary interventions were attempted including biopsy (n = 13), stone removal (n = 6), stent removal (n = 1), and intraductal electrohydraulic lithotripsy (n = 2) and were successful in 22 (88%). Other than two patients with procedure-related cholangitis with a mild grade of severity, no complications were observed.
Conclusions: Using a novel multi-bending prototype peroral direct cholangioscope, cholangioscopy had a high diagnostic and therapeutic success rate only when passed over a guidewire and anchoring balloon but not with the free-hand insertion technique. Comparative studies of direct cholangioscopy are warranted.
Keywords: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP); peroral direct cholangioscopy.
© 2013 The Authors. Digestive Endoscopy published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society.
Figures

References
-
- Larghi A, Waxman I. Endoscopic direct cholangioscopy by using an ultra-slim upper endoscope: A feasibility study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2006;63:853–857. - PubMed
-
- Park do H, Park BW, Lee HS, et al. Peroral direct cholangioscopic argon plasma coagulation by using an ultraslim upper endoscope for recurrent hepatoma with intraductal nodular tumor growth (with videos) Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007;66:201–203. - PubMed
-
- Moon JH, Ko BM, Choi HJ, et al. Intraductal balloon guided direct peroral cholangioscopy using an ultra-slim upper endoscope. Gastrointest. Endosc. 70:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Tsou YK, Lin CH, Tang JH, et al. Direct peroral cholangioscopy using an ultraslim endoscope and overtube balloon-assisted technique: A case series. Endoscopy. 2009;42:681–684. 2010. - PubMed
-
- Waxman I, Chennat J, Konda V. Peroral direct cholangioscopic-guided selective intrahepatic duct stent placement with an ultraslim endoscope. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010;71:875–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

