Novel amidines and analogues as promising agents against intracellular parasites: a systematic review
- PMID: 23561006
- PMCID: PMC3815587
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182013000292
Novel amidines and analogues as promising agents against intracellular parasites: a systematic review
Abstract
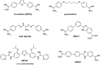
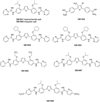
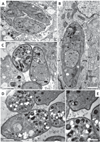
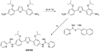
Parasitic protozoa comprise diverse aetiological agents responsible for important diseases in humans and animals including sleeping sickness, Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, malaria, toxoplasmosis and others. They are major causes of mortality and morbidity in tropical and subtropical countries, and are also responsible for important economic losses. However, up to now, for most of these parasitic diseases, effective vaccines are lacking and the approved chemotherapeutic compounds present high toxicity, increasing resistance, limited efficacy and require long periods of treatment. Many of these parasitic illnesses predominantly affect low-income populations of developing countries for which new pharmaceutical alternatives are urgently needed. Thus, very low research funding is available. Amidine-containing compounds such as pentamidine are DNA minor groove binders with a broad spectrum of activities against human and veterinary pathogens. Due to their promising microbicidal activity but their rather poor bioavailability and high toxicity, many analogues and derivatives, including pro-drugs, have been synthesized and screened in vitro and in vivo in order to improve their selectivity and pharmacological properties. This review summarizes the knowledge on amidines and analogues with respect to their synthesis, pharmacological profile, mechanistic and biological effects upon a range of intracellular protozoan parasites. The bulk of these data may contribute to the future design and structure optimization of new aromatic dicationic compounds as novel antiparasitic drug candidates.
Figures



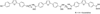

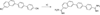
References
-
- Aly AA, Nour-El-Din AM. Functionality of amidines and amidrazones. Archive for Organic Chemistry. 2008:153–194.
-
- Ando M, Kamei R, Komagoe K, Inoue T, Yamada K, Katsu T. In situ potentiometric method to evaluate bacterial outer membrane-permeabilizing ability of drugs: example using antiprotozoal diamidines. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 2012;91:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Ansede JH, Voyksner RD, Ismail MA, Boykin DW, Tidwell RR, Hall JE. In vitro metabolism of an orally active O-methyl amidoxime prodrug for the treatment of CNS trypanosomiasis. Xenobiotica. 2005;35:211–226. - PubMed
-
- Arafa RK, Brun R, Wenzler T, Tanious FA, Wilson WD, Stephens CE, Boykin DW. Synthesis, DNA affinity, and antiprotozoal activity of fused ring dicationic compounds and their prodrugs. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2005;48:5480–5488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

