Extrapolating the effect of deleterious nsSNPs in the binding adaptability of flavopiridol with CDK7 protein: a molecular dynamics approach
- PMID: 23561625
- PMCID: PMC3726351
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-7-10
Extrapolating the effect of deleterious nsSNPs in the binding adaptability of flavopiridol with CDK7 protein: a molecular dynamics approach
Abstract
Background: Recent reports suggest the role of nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) gene associated with defect in the DNA repair mechanism that may contribute to cancer risk. Among the various inhibitors developed so far, flavopiridol proved to be a potential antitumor drug in the phase-III clinical trial for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Here, we described a theoretical assessment for the discovery of new drugs or drug targets in CDK7 protein owing to the changes caused by deleterious nsSNPs.
Methods: Three nsSNPs (I63R, H135R, and T285M) were predicted to have functional impact on protein function by SIFT, PolyPhen2, I-Mutant3, PANTHER, SNPs&GO, PhD-SNP, and screening for non-acceptable polymorphisms (SNAP). Furthermore, we analyzed the native and proposed mutant models in atomic level 10 ns simulation using the molecular dynamics (MD) approach. Finally, with the aid of Autodock 4.0 and PatchDock, we analyzed the binding efficacy of flavopiridol with CDK7 protein with respect to the deleterious mutations.
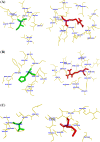
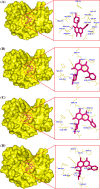
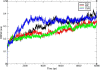
Results: By comparing the results of all seven prediction tools, three nsSNPs (I63R, H135R, and T285M) were predicted to have functional impact on the protein function. The results of protein stability analysis inferred that I63R and H135R exhibited less deviation in root mean square deviation in comparison with the native and T285M protein. The flexibility of all the three mutant models of CDK7 protein is diverse in comparison with the native protein. Following to that, docking study revealed the change in the active site residues and decrease in the binding affinity of flavopiridol with mutant proteins.
Conclusion: This theoretical approach is entirely based on computational methods, which has the ability to identify the disease-related SNPs in complex disorders by contrasting their costs and capabilities with those of the experimental methods. The identification of disease related SNPs by computational methods has the potential to create personalized tools for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of diseases.
Lay abstract: Cell cycle regulatory protein, CDK7, is linked with DNA repair mechanism which can contribute to cancer risk. The main aim of this study is to extrapolate the relationship between the nsSNPs and their effects in drug-binding capability. In this work, we propose a new methodology which (1) efficiently identified the deleterious nsSNPs that tend to have functional effect on protein function upon mutation by computational tools, (2) analyze d the native protein and proposed mutant models in atomic level using MD approach, and (3) investigated the protein-ligand interactions to analyze the binding ability by docking analysis. This theoretical approach is entirely based on computational methods, which has the ability to identify the disease-related SNPs in complex disorders by contrasting their costs and capabilities with those of the experimental methods. Overall, this approach has the potential to create personalized tools for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysing the Effect of Mutation on Protein Function and Discovering Potential Inhibitors of CDK4: Molecular Modelling and Dynamics Studies.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 7;10(8):e0133969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133969. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26252490 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the impact of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CDK2-flavopiridol complex by molecular dynamics analysis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013 Jul;66(3):681-95. doi: 10.1007/s12013-012-9512-5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23300027
-
Computational identification of pathogenic associated nsSNPs and its structural impact in UROD gene: a molecular dynamics approach.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Nov;70(2):735-46. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-9975-7. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24777812
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 inhibitors in cancer therapy.Future Med Chem. 2020 May;12(9):813-833. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2019-0334. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32208930 Review.
-
Targeting CDK7 in oncology: The avenue forward.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108229. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108229. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35700828 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico analysis of deleterious SNPs of human MTUS1 gene and their impacts on subsequent protein structure and function.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252932. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125870 Free PMC article.
-
Saudi Familial Hypercholesterolemia Patients With Rare LDLR Stop Gain Variant Showed Variable Clinical Phenotype and Resistance to Multiple Drug Regimen.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 25;8:694668. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.694668. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34249980 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive In Silico Analysis on the Structural and Functional Impact of SNPs in the Congenital Heart Defects Associated with NKX2-5 Gene-A Molecular Dynamic Simulation Approach.PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0153999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153999. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27152669 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of non-synonymous SNP on JAK1 protein structure and subsequent function.Bioinformation. 2019 Oct 26;15(10):723-729. doi: 10.6026/97320630015723. eCollection 2019. Bioinformation. 2019. PMID: 31831954 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and structural based approach to identify malignant nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with CDK4 gene.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 4;16(11):e0259691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259691. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34735543 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

