Suppression of nucleotide metabolism underlies the establishment and maintenance of oncogene-induced senescence
- PMID: 23562156
- PMCID: PMC3840499
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.004
Suppression of nucleotide metabolism underlies the establishment and maintenance of oncogene-induced senescence
Abstract
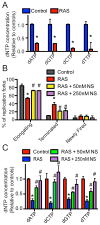
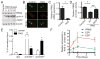
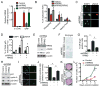
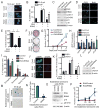
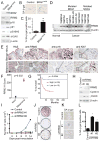
Oncogene-induced senescence is characterized by a stable cell growth arrest, thus providing a tumor suppression mechanism. However, the underlying mechanisms for this phenomenon remain unknown. Here, we show that a decrease in deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) levels underlies oncogene-induced stable senescence-associated cell growth arrest. The decrease in dNTP levels is caused by oncogene-induced repression of ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 (RRM2), a rate-limiting protein in dNTP synthesis. This precedes the senescence-associated cell-cycle exit and coincides with the DNA damage response. Consistently, RRM2 downregulation is both necessary and sufficient for senescence. Strikingly, suppression of nucleotide metabolism by RRM2 repression is also necessary for maintenance of the stable senescence-associated cell growth arrest. Furthermore, RRM2 repression correlates with senescence status in benign nevi and melanoma, and its knockdown drives senescence of melanoma cells. These data reveal the molecular basis whereby the stable growth arrest of oncogene-induced senescence is established and maintained through suppression of nucleotide metabolism.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
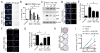

References
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444:633–637. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J. Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell. 2005;120:513–522. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J, d’Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:729–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

