Development and function of group 2 innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 23562755
- PMCID: PMC3776222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.02.010
Development and function of group 2 innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
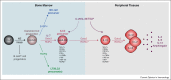
The innate lymphoid cell (ILC) family has recently expanded with the discovery of type-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2). These cells arise from lymphoid progenitors in the bone marrow and, under the control of the transcriptional regulators RORα and Gata3, they mature to give rise to IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13 producing ILC2. These cells are critical components of the innate immune response to parasitic worm infections and have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma and allergy. Recent advances in our understanding of the molecular regulation of ILC2 development and function now present the opportunity to develop new genetic models to assess ILC2 immune function and to investigate possible therapeutic interventions.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Spits H., Di Santo J.P. The expanding family of innate lymphoid cells: regulators and effectors of immunity and tissue remodeling. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Spits H., Artis D., Colonna M., Diefenbach A., Di Santo J.P., Eberl G., Koyasu S., Locksley R.M., McKenzie A.N., Mebius R.E. Innate lymphoid cells — a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:145–149. - PubMed
-
- Walker J.A., Barlow J.L., McKenzie A.N. Innate lymphoid cells — how did we miss them? Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Fort M.M., Cheung J., Yen D., Li J., Zurawski S.M., Lo S., Menon S., Clifford T., Hunte B., Lesley R. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity. 2001;15:985–995. - PubMed
-
- Hurst S.D., Muchamuel T., Gorman D.M., Gilbert J.M., Clifford T., Kwan S., Menon S., Seymour B., Jackson C., Kung T.T. New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol. 2002;169:443–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

