The influence of T cell Ig mucin-3 signaling on central nervous system autoimmune disease is determined by the effector function of the pathogenic T cells
- PMID: 23562810
- PMCID: PMC3678277
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300083
The influence of T cell Ig mucin-3 signaling on central nervous system autoimmune disease is determined by the effector function of the pathogenic T cells
Abstract
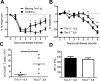
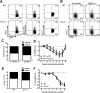
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the CNS mediated by self-reactive, myelin-specific T cells. Both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells play important roles in the pathogenesis of MS. MS is studied using experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model mediated by myelin-specific T cells. T cell Ig mucin-3 (Tim-3) is a cell surface receptor expressed on CD4(+) IFN-γ-secreting Th1 cells, and triggering Tim-3 signaling ameliorated EAE by inducing death in pathogenic Th1 cells in vivo. This suggested that enhancing Tim-3 signaling might be beneficial in patients with MS. However, Tim-3 is also expressed on activated CD8(+) T cells, microglia, and dendritic cells, and the combined effect of manipulating Tim-3 signaling on these cell types during CNS autoimmunity is unknown. Furthermore, CD4(+) IL-17-secreting Th17 cells also play a role in MS, but do not express high levels of Tim-3. We investigated Tim-3 signaling in EAE models that include myelin-specific Th17, Th1, and CD8(+) T cells. We found that preventing Tim-3 signaling in CD4(+) T cells altered the inflammatory pattern in the CNS due to differential effects on Th1 versus Th17 cells. In contrast, preventing Tim-3 signaling during CD8(+) T cell-mediated EAE exacerbated disease. We also analyzed the importance of Tim-3 signaling in EAE in innate immune cells. Tim-3 signaling in dendritic cells and microglia did not affect the manifestation of EAE in these models. These results indicate that the therapeutic efficacy of targeting Tim-3 in EAE is dependent on the nature of the effector T cells contributing to the disease.
Figures
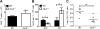
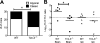
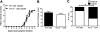
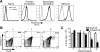
Similar articles
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells and activation of microglia in the CNS during the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 May;24(4):641-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.01.014. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20138983
-
Lineage-Specific Metabolic Properties and Vulnerabilities of T Cells in the Demyelinating Central Nervous System.J Immunol. 2017 Jun 15;198(12):4607-4617. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600825. Epub 2017 May 15. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28507026 Free PMC article.
-
IL-7/IL-7 Receptor Signaling Differentially Affects Effector CD4+ T Cell Subsets Involved in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):1974-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403135. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26223651 Free PMC article.
-
Using EAE to better understand principles of immune function and autoimmune pathology.J Autoimmun. 2013 Sep;45:31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 9. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23849779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TIM-3 Rs10515746 (A/C) and Rs10053538 (C/A) Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis.Iran J Public Health. 2016 May;45(5):644-9. Iran J Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27398337 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of T cells in multiple sclerosis: what do we currently know?J Neurol. 2021 Dec;268(12):4587-4593. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10275-x. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33083867 Review.
-
T cell exhaustion: from pathophysiological basics to tumor immunotherapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Jan 5;15(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12964-016-0160-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28073373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TIM-3 is not essential for development of airway inflammation induced by house dust mite antigens.Allergol Int. 2016 Oct;65(4):459-465. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 18. Allergol Int. 2016. PMID: 27209052 Free PMC article.
-
The yin and yang of co-inhibitory receptors: toward anti-tumor immunity without autoimmunity.Cell Res. 2020 Apr;30(4):285-299. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0277-x. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31974523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson AC, Anderson DE, Bregoli L, Hastings WD, Kassam N, Lei C, Chandwaskar R, Karman J, Su EW, Hirashima M, Bruce JN, Kane LP, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA. Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science. 2007;318:1141–1143. - PubMed
-
- Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, Ryu A, Waldner H, Chernova T, Manning S, Greenfield EA, Coyle AJ, Sobel RA, Freeman GJ, Kuchroo VK. Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature. 2002;415:536–541. - PubMed
-
- Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong HB, Imitola J, Khoury SJ, Zheng XX, Strom TB, Kuchroo VK. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nature Immunology. 2005;6:1245–1252. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Langrish CL, McKenzie B, Joyce-Shaikh B, Stumhofer JS, McClanahan T, Blumenschein W, Churakovsa T, Low J, Presta L, Hunter CA, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. Anti-IL-23 therapy inhibits multiple inflammatory pathways and ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1317–1326. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

